
Prepaid Salary Journal Entry
Prepaid expenses are current assets. The adjusting entry for prepaid expense will depend upon the initial journal entry, whether it was recorded using the asset method or expense method. The adjusting entry if the asset method was used is: Dr Expense account. Cr Prepaid expense account. for the amount incurred.

Prepaid Expense Dalam Akuntansi Bisnis, Apa Itu?
Prepaid Expense Examples. Let's look at some examples of prepaid expenses and see how and why they are recorded. Example 1. Most prepaid costs include monthly utility bills, rent and insurance. Let's look at insurance as an example. Let's say that Bill's Retail Store pays its insurance premiums every six months.
Mencatat Prepaid Expense dan Amortisasi Mekari Jurnal
Types of Prepaid Expenses. Common examples of prepaid expenses include: Rent: If a company pays rent for office space in advance, it is recorded as a prepaid expense until the period covered by the rent payment is reached. Insurance premiums: When a company pays for insurance coverage upfront, it is considered a prepaid expense and recognized as an expense only as the coverage period occurs.

What is Prepaid expense Example Journal Entry Tutor's Tips
In this accounting lesson, we explain what prepaid expense is, how it is adjusted, and how to record it in a journal entry. Check it out.Accrued Expense Expl.

(PDF) Adjusting Journal Entries Prepaid Expenses adler gabriel Academia.edu
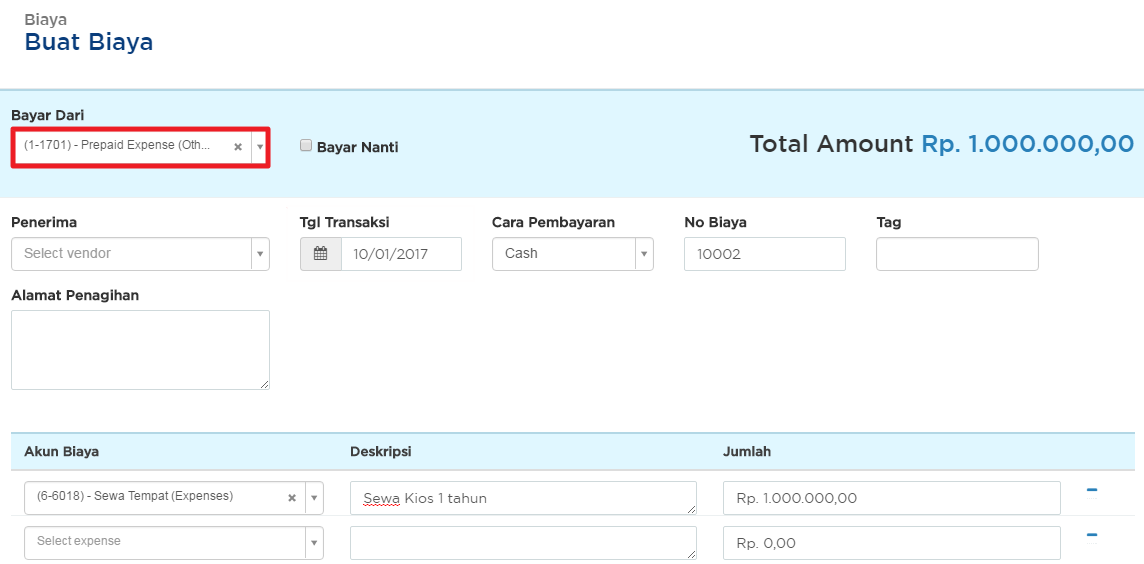
Prepaid expense atau biaya dibayar di muka adalah biaya yang dibayar di muka sebelum menerima produk atau layanan.Setiap kali Anda membayar sesuatu di muka, Anda harus mencatatnya di buku Anda sebagai jurnal biaya dibayar di muka. Prepaid expense juga dikenal sebagai biaya yang ditangguhkan.Mencatat pengeluaran ini adalah bagian dari proses akuntansi akrual.
Free Prepaid Expense Schedule Excel Template Printable Templates
ABC Ltd. can make the prepaid expense journal entry for office supplies on June 15, 2020, as below: In this journal entry, the supplies account is a prepaid expense that will be recognized as an expense when it is used. Likewise, the $5,000 is recorded as a prepaid expense in the current asset of the balance sheet.

Prepaid Expense Pengertian, Contoh, dan Cara Menjurnalnya
Read More »Jurnal Biaya Dibayar Dimuka (Prepaid Expense) Dalam metode pencatatan akuntansi secara akural, biaya dibayar dimuka merupakan beban yang dikapitalisasi, artinya beban tersebut pada saat uang kasnya dikeluarkan dicatat sebagai aset di neraca karena beban tersebut belum terjadi. Biaya disini bukanlah uang muka atau down payment.
Journal Entry for Prepaid Insurance Online Accounting
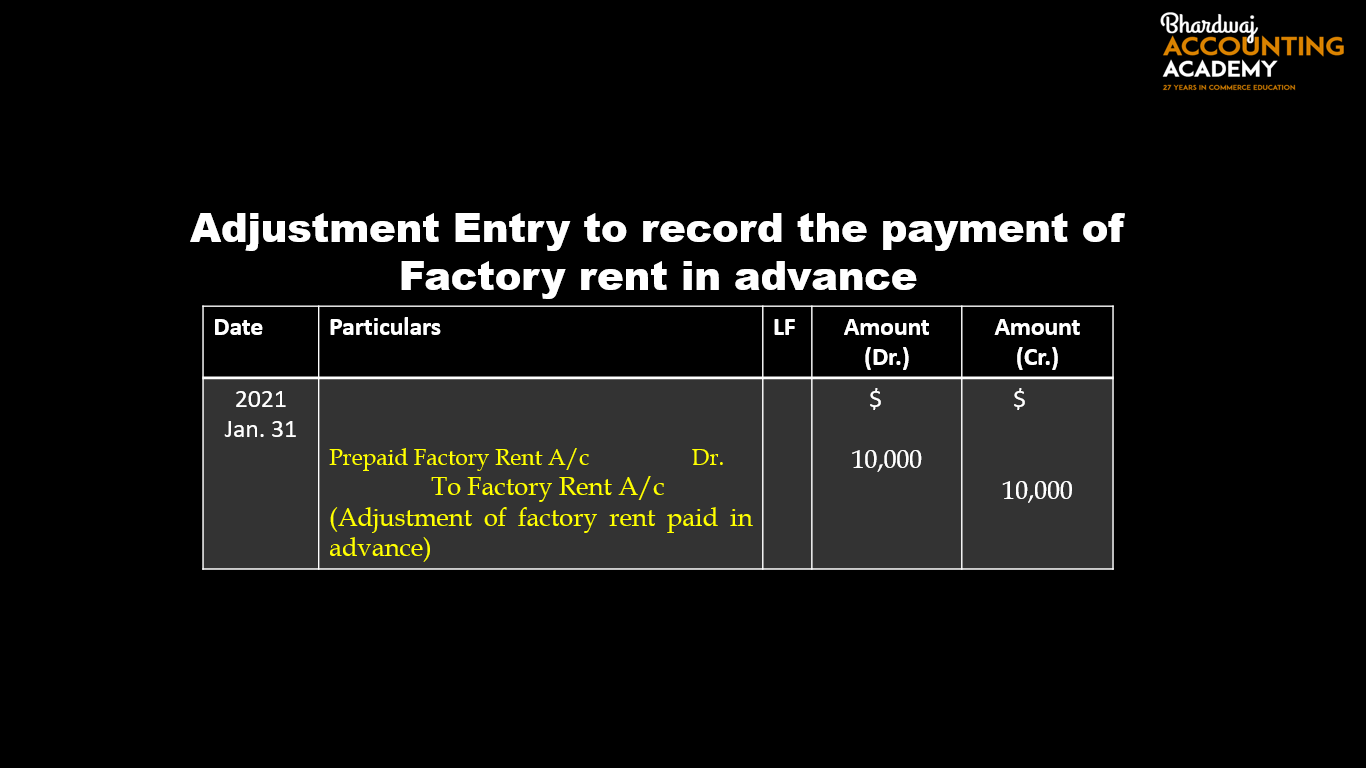
Since the prepayment is for six months, divide the total cost by six ($9,000 / 6). Adjust your accounts by $1,500 each month. Expense $1,500 of the rent with a debit. Reduce the Prepaid Expense account with a credit. Repeat the process each month until the rent is used and the asset account is empty.

Prepaid Expense Pengertian, Contoh, dan Cara Menjurnalnya
Prepaid Insurance. Prepaid insurance is a key component of business accounting, whereby advance payments are made for insurance coverage. This involves a business paying for insurance coverage upfront for a specified duration, typically ranging from a few months to a year. The payment is usually recorded as a prepaid expense on the balance.
Prepaid expense journal entry important 2022
Examples of Prepaid Expenses. Examples of prepaid expenses include: Paying for a subscription for a year upfront because they were offering a large discount. Signing a 12-month lease for office space that requires 6 months of upfront payment. Paying for a 24-month insurance policy for office space with cash upfront.

Prepaid Expense Explained With Journal Entry and Adjusting Entry Example YouTube
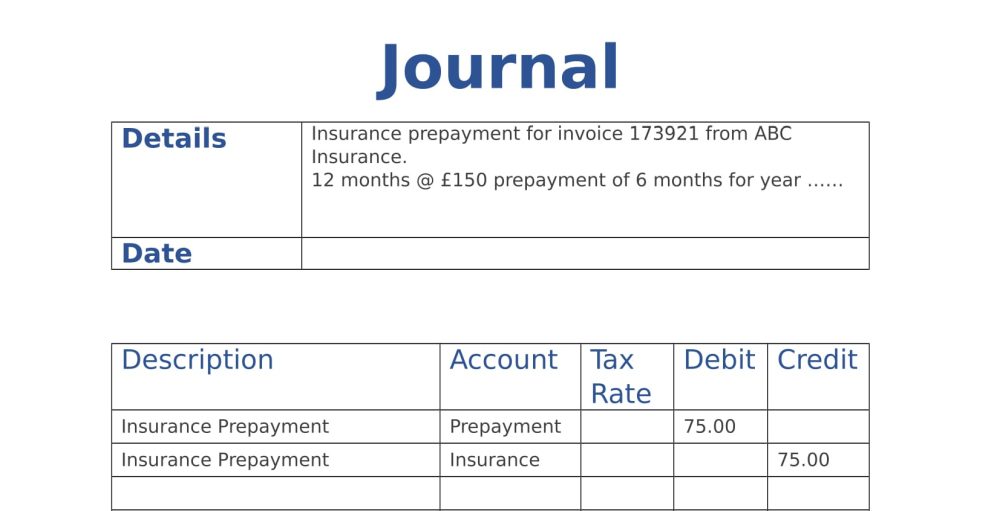
The initial entry is a debit of $12,000 to the prepaid insurance (asset) account, and a credit of $12,000 to the cash (asset) account. If you want to create a prepaid expenses journal entry, the best method is to identify the expenses first and use adjusting entries. The advance payment of expenses does not provide value right away.

Jurnal Penyesuaian Deferrals Prepaid expenses (beban dibayar dimuka) Part 1 YouTube
A prepaid expense is an expense that has been paid in advance but from which no gain has yet been realized. When a business pays in advance for products or services that will be received in the future, the prepaid expenses are recorded as assets on the balance sheet. Prepaid expenses are originally listed as assets, but as time passes, their.

Journal Entry for Prepaid Expenses
Recording a journal entry for prepaid expenses involves the following steps. STEP # 1: First of all, the entity has to fully pay the expense. To record the full amount of prepayment a simple journal entry is made where we have to debit the prepaid expense account as it is an asset for us as discussed earlier and an increase in the asset is.
Mencatat Prepaid Expense dan Amortisasi Mekari Jurnal
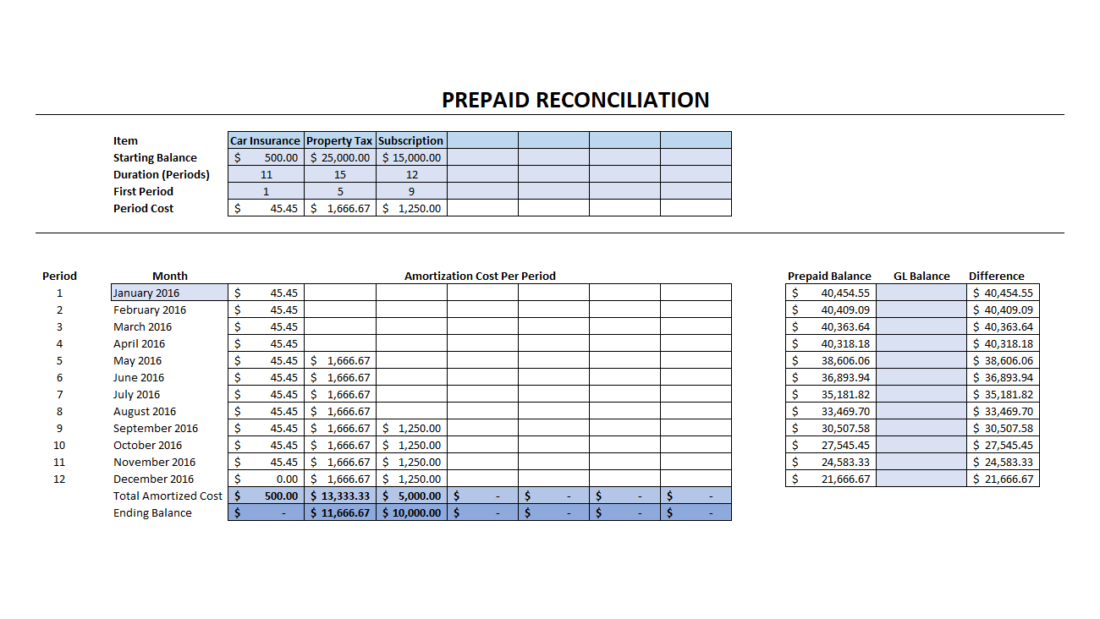
The correct insurance expenses for 2019 comprise 4/12th of $4,800 = $1,600. The balance, $3,200 (4,800 - 1,600), relates to 2020 and should be charged to that year's profit and loss account. Although Mr. John's trial balance does not disclose it, there is a current asset of $3,200 on 31 December 2019.

Free Prepaid Expense Schedule Excel Template Printable Form, Templates and Letter
Below is the journal entry for prepaid expenses; According to the three types of accounts in accounting "prepaid expense" is a personal account. Prepaid Expense A/C. Debit. Debit the increase in asset. To Expense A/C. Credit. Credit the decrease in expense. It involves two accounts: Prepaid Expense Account and the related Expense Account.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/prepaid-expense-4191042-final-936e813abfe74ae8a62880f4be96eb52.png)
Prepaid Expense Definition and Example
Prepaid expenses, or Prepaid Assets as they are commonly referred to in general accounting, are recognized on the balance sheet as an asset. A "prepaid asset" is the result of a prepaid expense being recorded on the balance sheet. Prepaid expenses result from one party paying in advance for a service yet to be performed or an asset yet to.