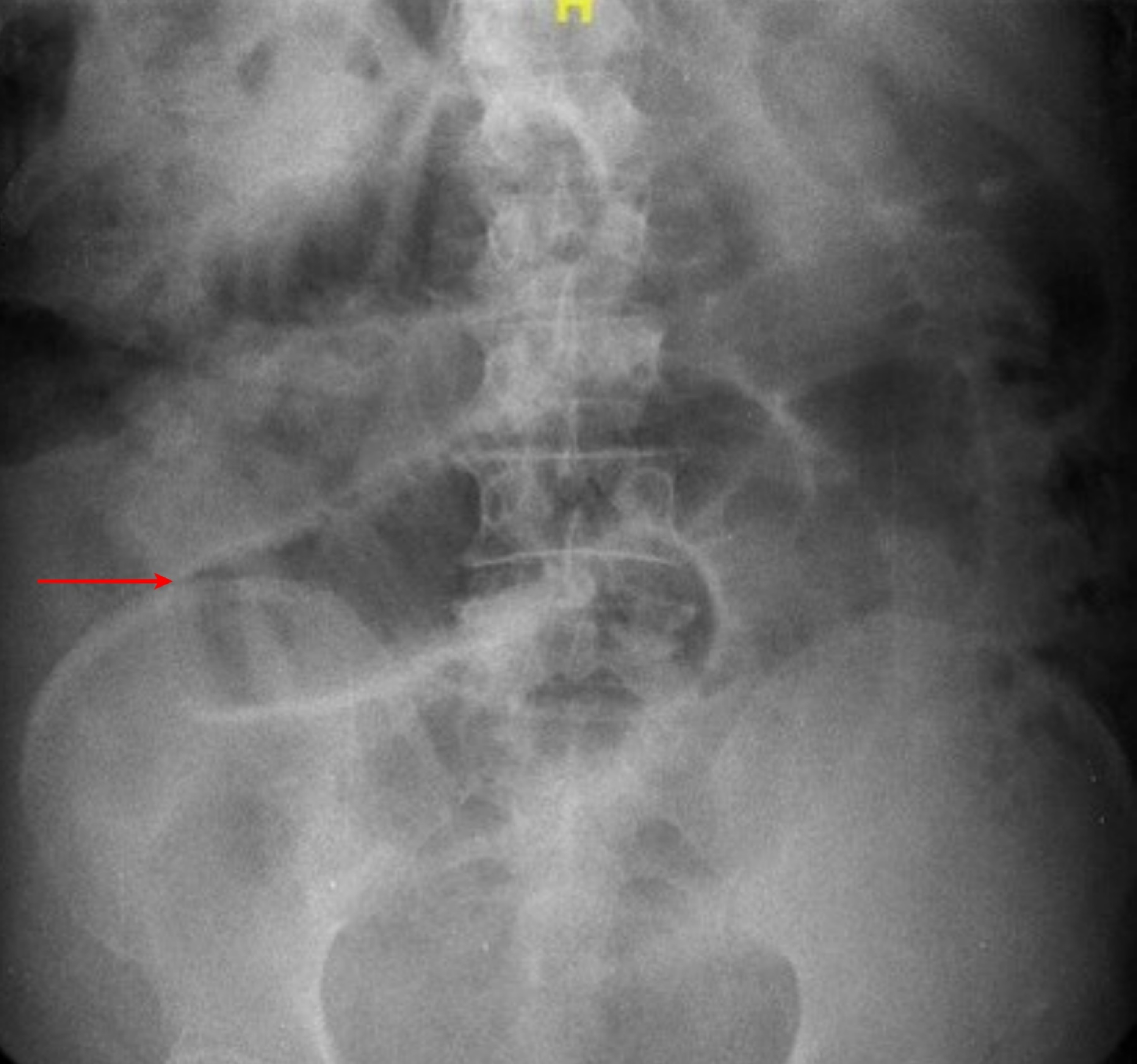
Cureus Strangulated Falciform Hernia
Hernias are abnormal bulges or openings in the fascia of the abdominal wall. These defects can be present in any area of the abdominal wall fascia where there is an anatomic weakening present. Hernias are commonly located on the anterior abdominal wall (umbilical) and groin regions (inguinal, femoral). Hernias are classified as reducible when the contents within the hernia can be placed intra.

Strangulated Umbilical Hernia with Abscess Formation Ultrasound Doppler Case 199 YouTube
bloody stools. constipation. darkening or reddening of the skin over the hernia. fatigue. fever. inability to pass gas. inflammation or tenderness around the hernia. increased heart rate. nausea.

Strangulated Hernia G & L Surgical Clinic Dr Ganesh Ramalingam
Incarcerated (also referred to as irreducible) is used to describe herniae, in which their contents are unable to pass back through the hernial opening to their anatomical site of origin 5 . Incarceration is a risk factor for bowel obstruction and strangulation, and therefore usually necessitates urgent surgery 5.

Strangulated hernia with bowel ischaemia Radiology Case
A hernia may only look like a slight bulge or protrusion, but it can have serious, even life-threatening, effects. A strangulated hernia, one of the most serious hernia-related disorders, can seriously endanger your health if left untreated. You may navigate this medical emergency with confidence because of the Iskandar Complex Hernia Center's recognized knowledge and unmatched empathy.
Strangulated Hernia Symptoms, Treatment, Outlook, and More
A strangulated hernia repair is an emergency. The surgeon's priority is to 'reduce' the hernia, which means to release the entrapped bowel and return it where it belongs, inside the abdominal cavity. That must be done before the tissue is permanently damaged, which would be an extremely unpleasant complication.
Strangulated Hernia Symptoms HRF
Hernia. A hernia usually happens in your abdomen or groin, when one of your organs pushes through the muscle or tissue that contains it. It may look like an odd bulge that comes and goes during different activities or in different positions. It may or may not cause symptoms, such as discomfort or pain. Most hernias eventually will need surgical.

Strangulated hernia with bowel ischaemia Radiology Case
Strangulated in the context of hernias refers to an incarcerated hernia in which the hernial opening is so constricted that the arterial supply is compromised, leading to ischemia and eventually gangrene.It is a surgical emergency. Although strangulated bowel is also often obstructed, this is not always the case. The most common groin hernia that can be strangulated is the femoral hernia.

Strangulated hernia with bowel ischaemia Radiology Case
A strangulated hiatal hernia is a medical emergency. Learn the symptoms and why they occur. A strangulated hiatal hernia is a medical emergency. It occurs when the hernia slips up through the diaphragm, is unable to slip back through, and gets trapped. This can cut off blood supply and cause the tissue to die.
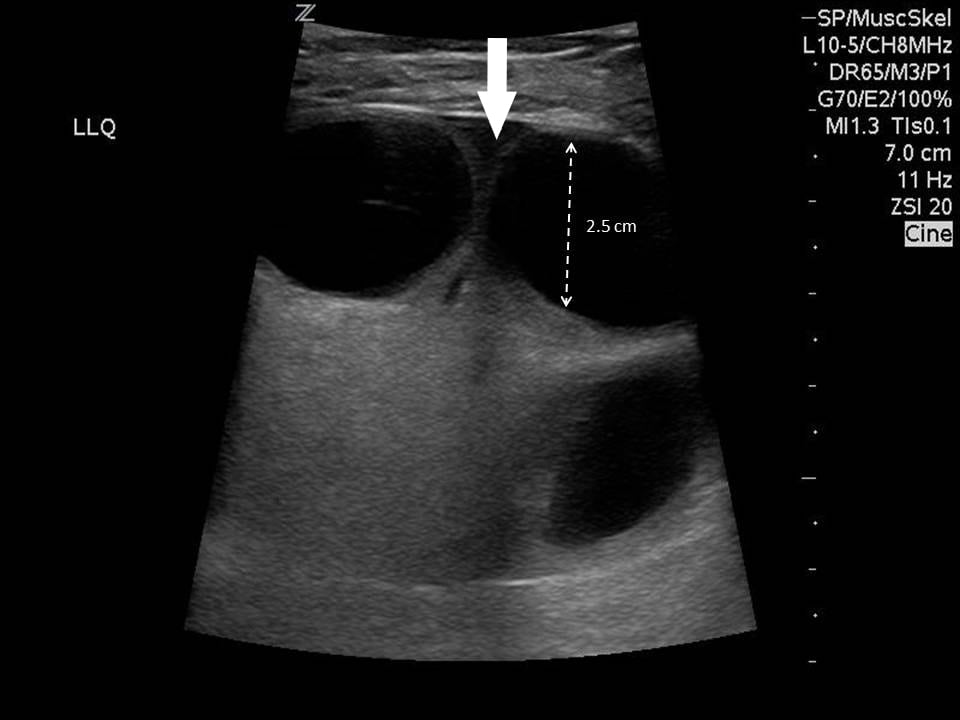
Diagnosis of a Strangulated Laparoscopic Incisional Hernia with PointofCare Ultrasonography
Strangulated inguinal hernia occurs when part of the hernia becomes irreducible and subsequently causes bowel ischemia secondary to a reduction in blood flow to the hernia. Therefore, management strategy differs and depends on the presentation of the hernia, duration, patient, and surgical factors. One thing is for sure: conservative management is not recommended for a strangulated inguinal.

Strangulated hernia with bowel ischemia Image
Strangulated inguinal hernias occur when the contents of a hernia are deprived of adequate blood supply. This may occur in both acutely and chronically incarcerated hernias. Strangulation is quite rare, but when it occurs, it is a true hernia emergency necessitating immediate operation. The mortality rate in strangulated inguinal hernias may be.
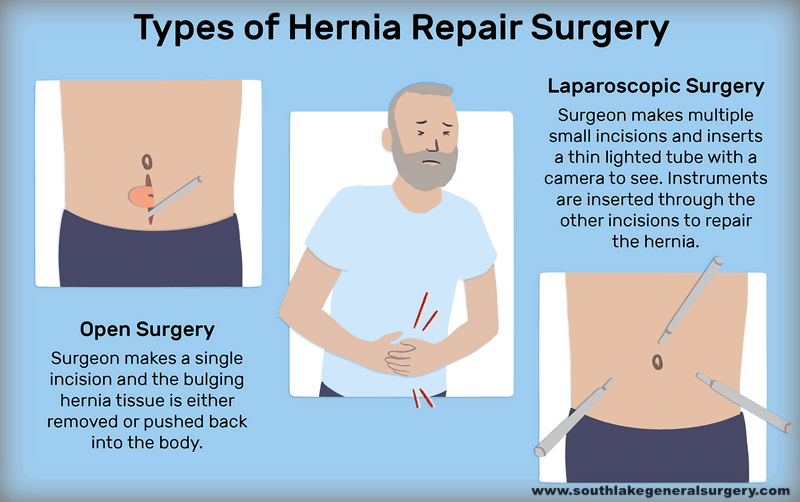
Learn about Six types of Hernia Southlake General Surgery
Symptoms. Inguinal hernia signs and symptoms include: A bulge in the area on either side of your pubic bone, which becomes more obvious when you're upright, especially if you cough or strain. A burning or aching sensation at the bulge. Pain or discomfort in your groin, especially when bending over, coughing or lifting.

Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan of the strangulated hernia in... Download Scientific
Introduction. In our practice in Kumasi, strangulated inguinal hernia is a common cause of acute surgical admission for abdominal emergency second only to abdominal pain. 1 Strangulated inguinal hernia is the most important cause of acute small bowel obstruction accounting for 49% of the cases studied in Kumasi. 2 Surgery for strangulation is associated with 5-10 fold increase in morbidity.
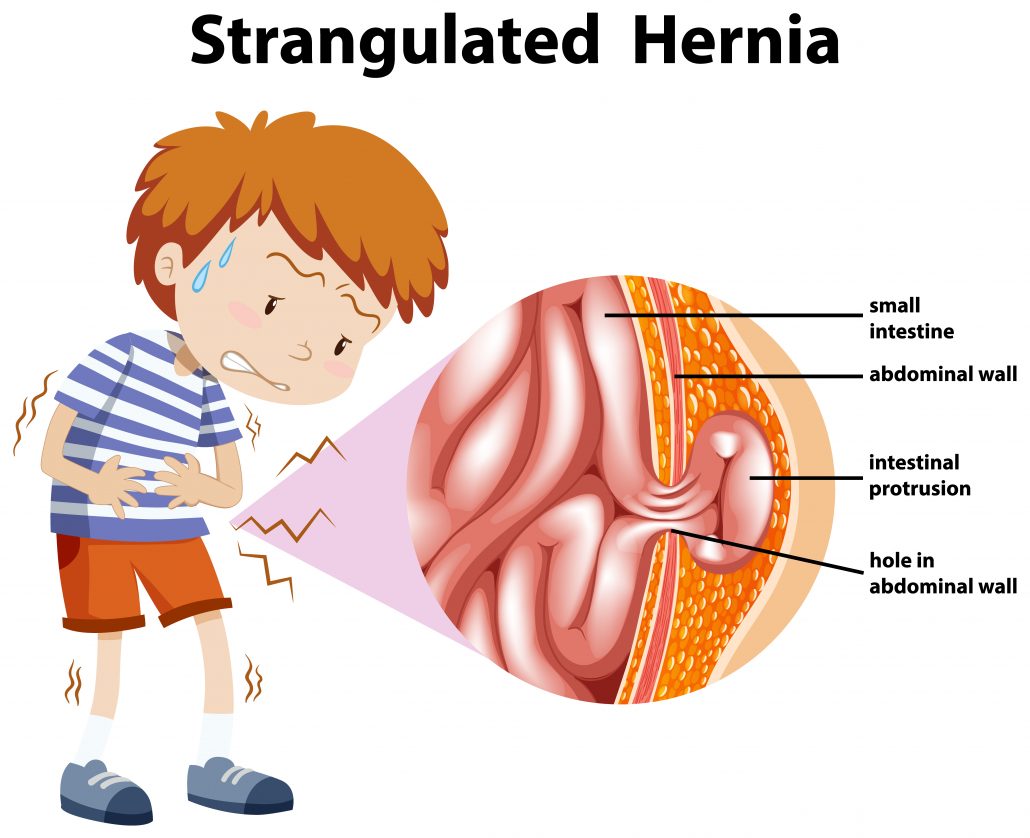
What is Hernia? and It’s Types Doss India
Strangulated inguinal hernia can be managed in a routine fashion. Three Classical approaches are described for an open repair of femoral hernia [ 1 ]. Low (Lockwood's), inguinal (Lotheissen's) and high (Mc Evedy's). Each approach describes a separate incision and dissection to access the femoral sac.
Hernia, strangulated and reducible. With cure by subcutaneous injections, together with
general fatigue. inflammation and color changes in the skin near the hernia. burning feeling around the hernia. nausea. vomiting. inability to pass gas. severe constipation or an inability to have.
Symptoms, Treatments & Prevention of Strangulated Hernia
Strangulated inguinal hernia is a life-threatening condition which requires urgent surgical intervention. Historically, the prominence of "adhesive bands" as a cause of intestinal obstruction was already known, and was also the main historical cause of small intestinal obstruction before the advent of anesthesia.

How Does a Strangulated Hernia Feel? Alan Woodward Surgical Group
Symptoms. Inguinal hernia signs and symptoms include: A bulge in the area on either side of your pubic bone, which becomes more obvious when you're upright, especially if you cough or strain. A burning or aching sensation at the bulge. Pain or discomfort in your groin, especially when bending over, coughing or lifting.