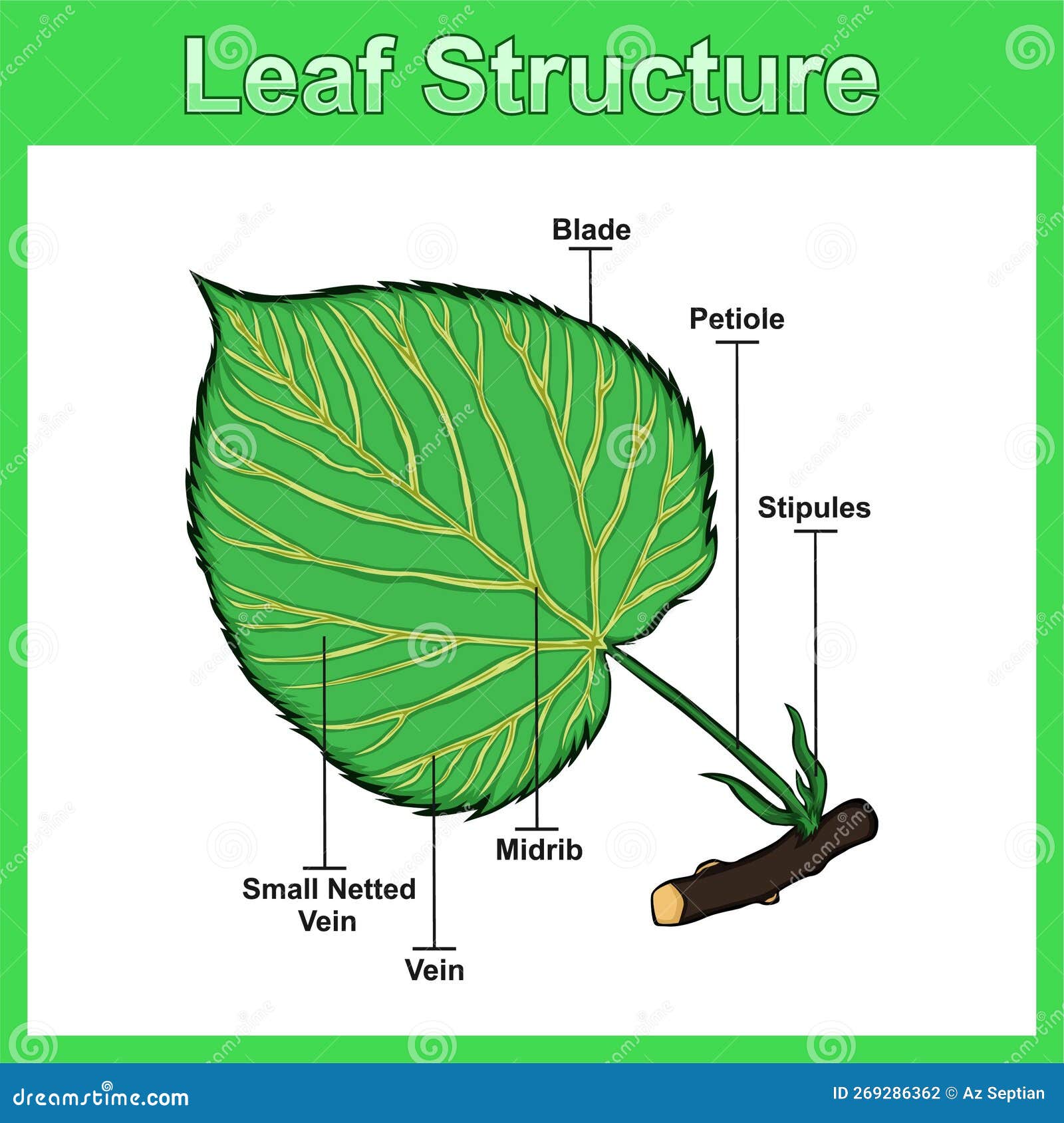
Leaf Structure Diagram, Structure Leaf Vector Illustration. Stock Vector Illustration of
Leaf Structure and Function Factories for Photosynthesis. A leaf is a highly organized factory - an organ constructed of several kinds of specialized tissues, each of which has its own duties.. of nutrients such as nitrogen from sunlight damage as they are relocated to other parts of the plant before the leaf is lost. This diagram also.

32 Label A Leaf Diagram Labels 2021
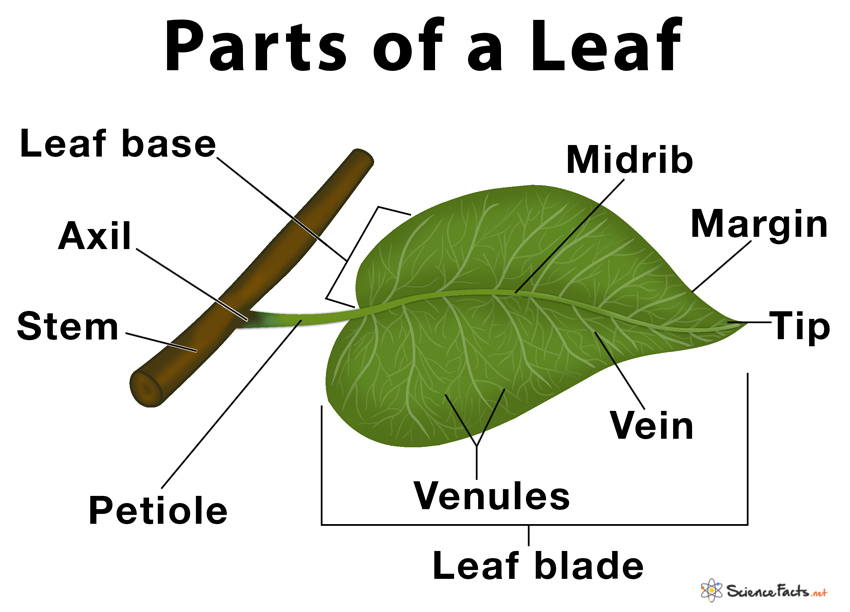
The petiole is a stem that attaches the leaf blade to the main stem of the plant. As plants have radiated, diversified, and adapted to different environments, you'll see that there are many variations on this theme. The photo on the left is a palmate leaf, the diagram on the right is a pinnate leaf. Photo by Maria Morrow, CC-BY 4.0. Diagram on.
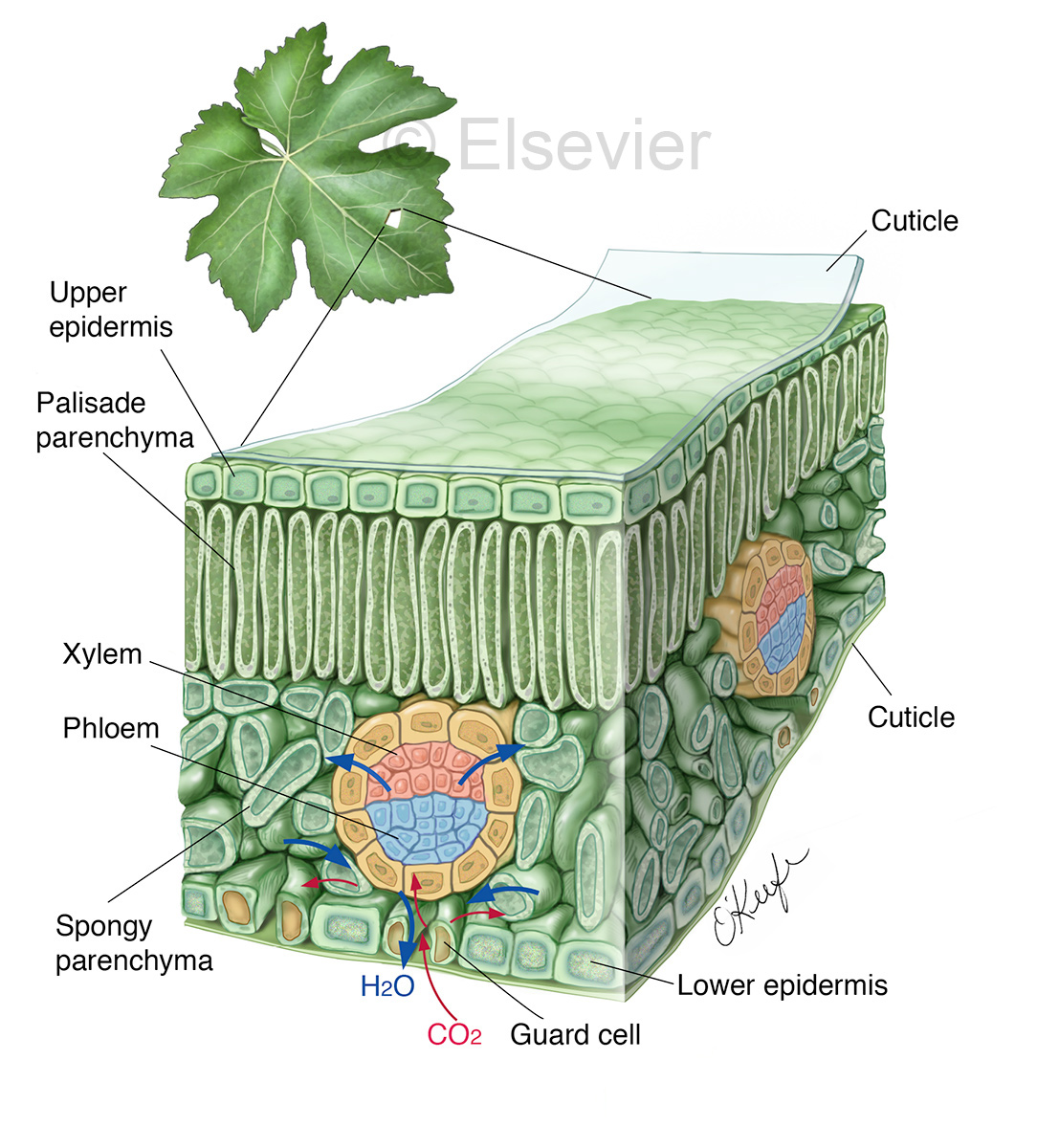
Biomedical Illustrator Medical & Biological Illustrations Laurie O’Keefe
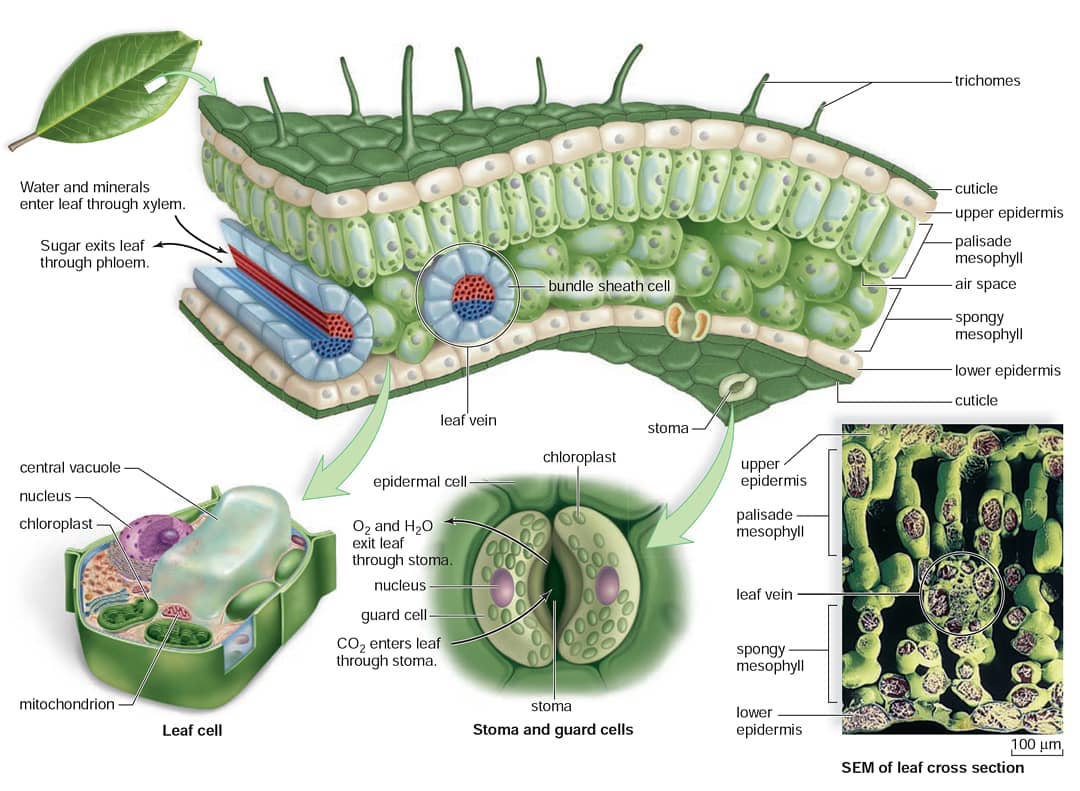
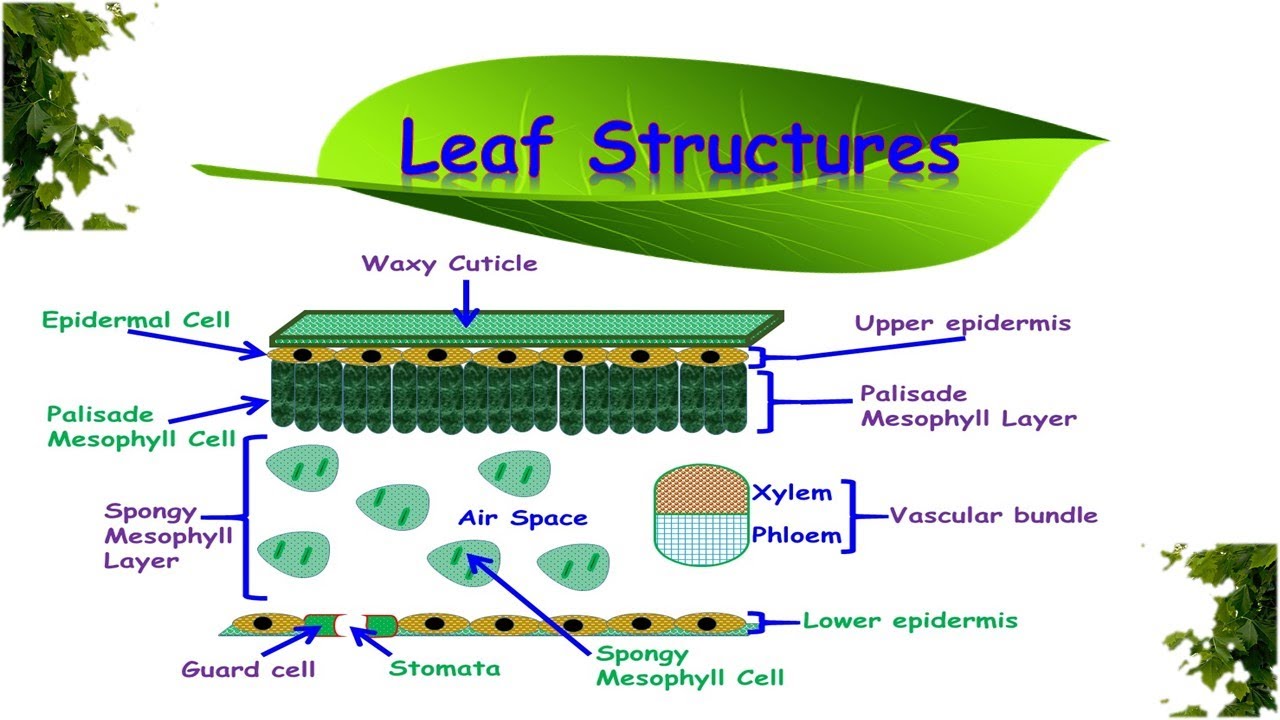
Figure 30.10.1 30.10. 1: Mesophyll: (a) (top) The central mesophyll is sandwiched between an upper and lower epidermis. The mesophyll has two layers: an upper palisade layer and a lower spongy layer. Stomata on the leaf underside allow gas exchange. A waxy cuticle covers all aerial surfaces of land plants to minimize water loss.

Labeled Diagram Of A Leaf hubpages
Leaf parts and directional terms. Left: Diagram of a simple leaf showing the basic parts, including the petiole (stalk), lamina (blade), veins (strands of vascular tissue), margin (edge of the lamina), apex of the lamina, and base of the lamina.Right: Diagram of a leaf attached to a stem showing terms for directionality: adaxial (upper leaf surface), abaxial (lower leaf surface), proximal.
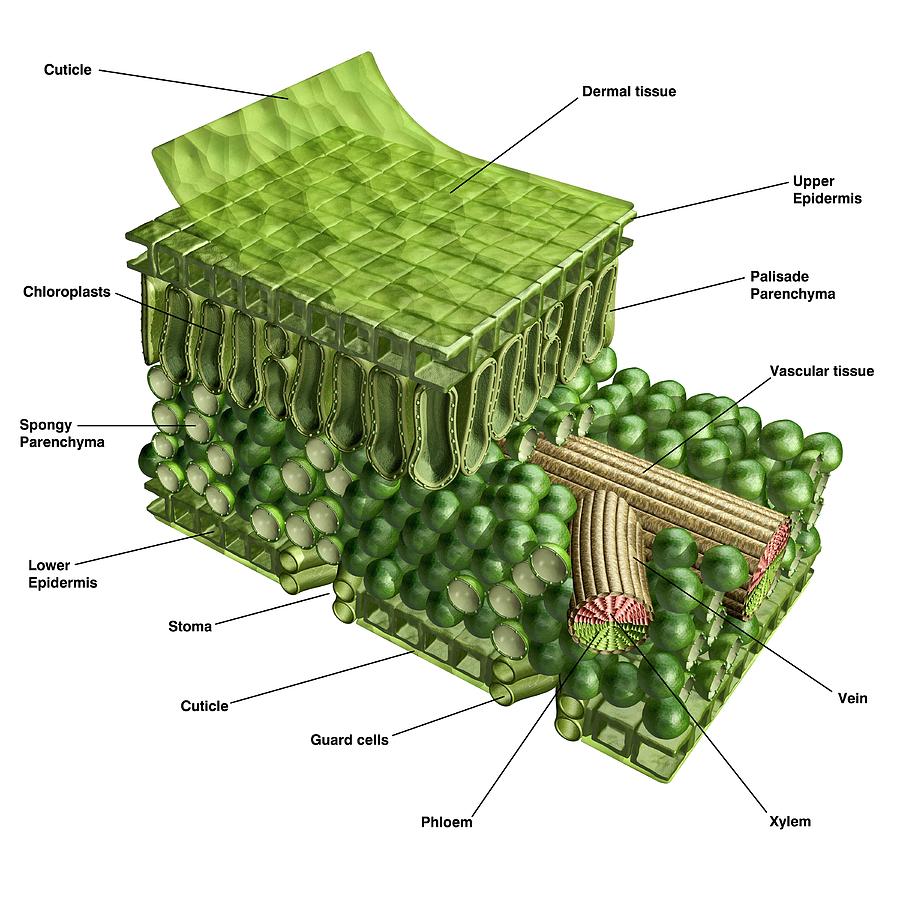
Plant Leaf Cross Section
The table below describes the different structures in a leaf and their functions; Leaf Structures Table. Diagram showing the cross-section of a leaf. The specialised cells in leaves have adaptive features which allow them to carry out a particular function in the plant;. 6.2.3 Structure of the Leaf; 6.2.4 Living in Extreme Conditions;
Leaf Structure and Photosynthesis YouTube
Figure 9.3. 2: Cross section of a hydrophytic leaf. Observe a prepared slide of a hydrophyte, such as Nymphaea, commonly called a water lily. Note the thin epidermal layer and the absence of stomata in the lower epidermis. In the spongy mesophyll, there are large pockets where air can be trapped.

Leaf Structure, Types, Functions GCSE Biology Revision
Q1. The stalk of leaf is called A. Sessile B. Plumule C. Stipule D. Petiole. Answers: Petiole is the stalk of a leaf that attaches the blade to the stem. In petiolate leaves, the leaf stalk is long. It is the structure through which products of photosynthesis are moved from leaves to the entire plant. So, the correct answer is 'Petiole' Q2.
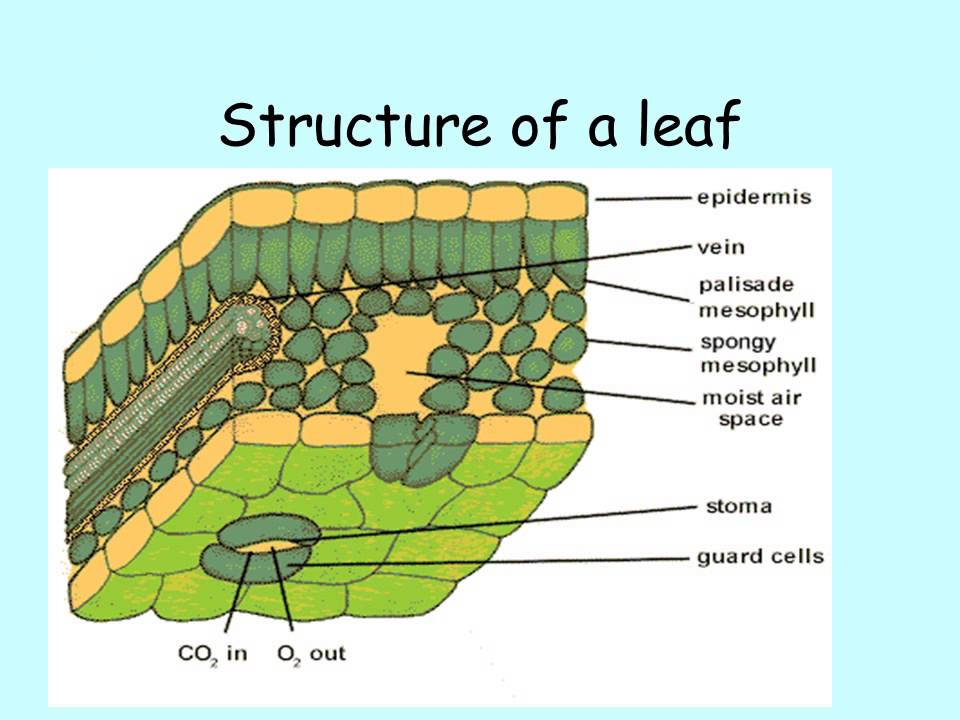
Structure of a leaf
A leaf is a compromise between two conflicting evolutionary pressures. The first is to expose a maximum photosynthetic surface to sunlight; the second is to conserve water while, at the same time, providing for the exchange of gases necessary for photosynthesis. The photosynthetic cells of leaves are of a general type known as parenchyma.
.PNG)
Plant structure adaptations and responses Presentation Plants, Animals, and Ecosystems
The main function of a leaf is to produce food for the plant by photosynthesis. Chlorophyll, the substance that gives plants their characteristic green colour, absorbs light energy.The internal structure of the leaf is protected by the leaf epidermis, which is continuous with the stem epidermis.The central leaf, or mesophyll, consists of soft-walled, unspecialized cells of the type known as.

Leaves Biology for Majors II
Lára has a particular interest in the area of infectious disease and epidemiology, and enjoys creating original educational materials that develop confidence and facilitate learning. 2.21 Leaf: Structure & Adaptations. FREE Biology revision notes on The Unifying Characteristics of Living Organisms. Designed by the teachers at SAVE MY EXAMS for.

Internal Structure of a Leaf DanicateMullen
The structure of a leaf is described below in detail : Parts of a Leaf. Generally, leaf base, petiole, and lamina, together form the main parts of a leaf. Leaf Base: This is the part where a leaf attaches to the stem. Leaf base has two small leaf-like structure called stipules.
Leaf Structures & Functions YouTube
Leaves are the powerhouse of plants. In most plants, leaves are the major site of food production for the plant. Structures within a leaf convert the energy in sunlight into chemical energy that the plant can use as food. Chlorophyll is the molecule in leaves that uses the energy in sunlight to turn water (H 2 O) and carbon dioxide gas (CO 2.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/leaf_crossection-57bf24a83df78cc16e1f29fd.jpg)
Plant Leaves and Leaf Anatomy
Figure 30.8.1 30.8. 1: Parts of a leaf: A leaf may seem simple in appearance, but it is a highly-efficient structure. Petioles, stipules, veins, and a midrib are all essential structures of a leaf. Within each leaf, the vascular tissue forms veins. The arrangement of veins in a leaf is called the venation pattern.
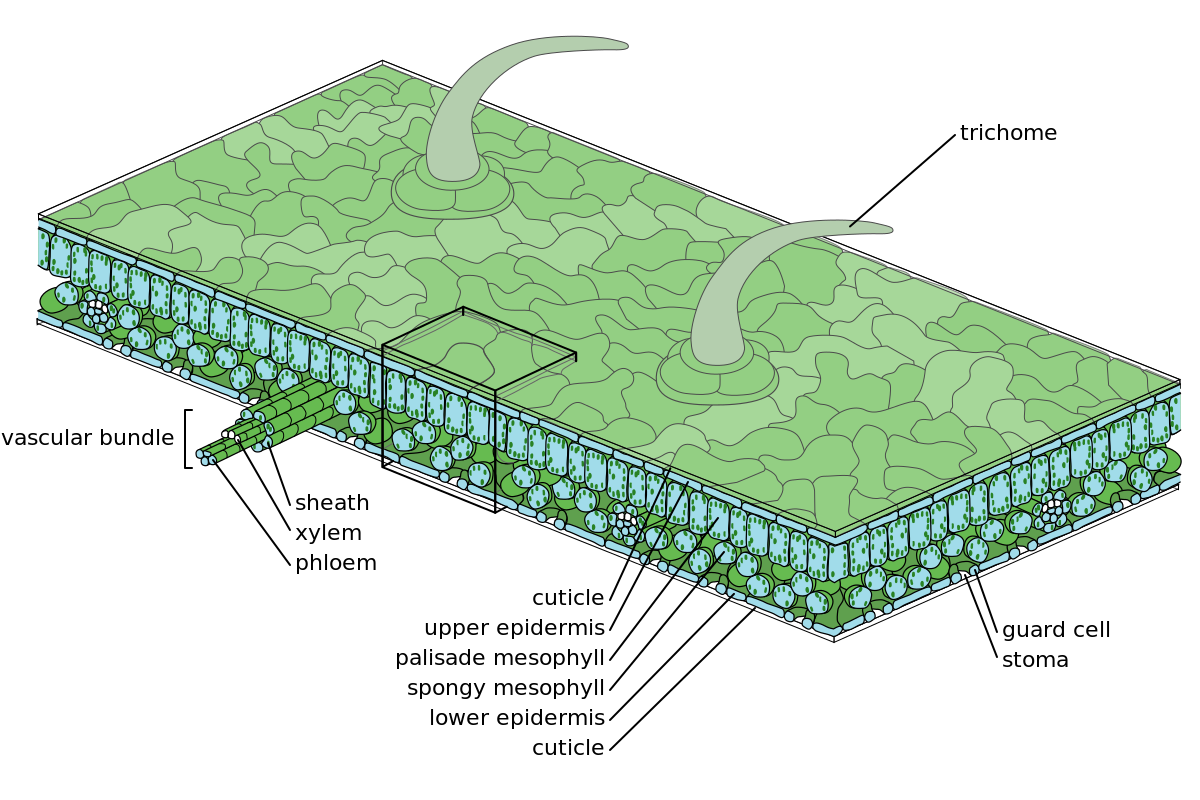
FileLeaf Structure.svg Wikipedia
Like the stem, the leaf contains vascular bundles composed of xylem and phloem (Figure 3.4.2.6 − 7 3.4.2. 6 − 7 ). When a typical stem vascular bundle (which has xylem internal to the phloem) enters the leaf, xylem usually faces upwards, whereas phloem faces downwards. The conducting cells of the xylem (tracheids and vessel elements.
25+ Label The Parts Of Leaf AntoniusNeiko
A typical leaf shows three main parts: 1) petiole, 2) leaf base, and 3) leaf blade or lamina, each performing specific functions. Parts of a Leaf Diagram. 1. Petiole. It is the stalk that connects a leaf to the stem of the plant, it is made of complex conducting tissues called vascular tissues.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/parts_of_a_leaf-56abaed23df78cf772b5625a.jpg)
Plant Leaves and Leaf Anatomy
The structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis close photosynthesis A chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water.