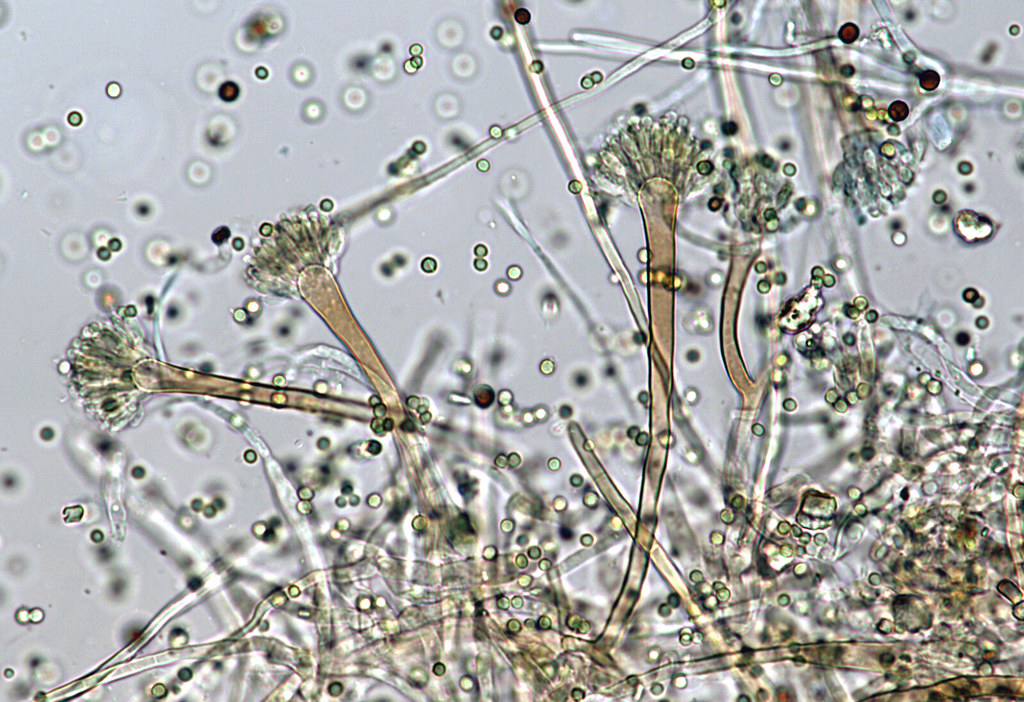

eeny weeny Aspergillus Perhaps this is Aspergillus nidulan… Flickr
Aspergillus (Mold!) under the Microscope Aspergillus consists of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. First catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli, the fungi when viewed under the microscope reminded him of the shape of an aspergillum, or holy water sprinkler.

Aspergillus_niger_SEM Aspergillus niger, Things under a microscope
Table of Contents Classification Aspergillus flavus Aspergillus fumigatus Aspergillus niger Aspergillus terreus Aspergillus glaucus Aspergillus nidulans Clinical Features of Aspergillus 1. Pulmonary Diseases a) Allergic Aspergillosis i) Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)

Aspergillus Under the microscope mycosis microbiology Mycose
Staining methodology The oldest specific preparation for microscopy is a concentrated (10-20%) potassium hydroxide solution, which softens keratin and allows direct visualisation of fungi and some morphology evaluation. Gram stains are less sensitive. Papanicolau stains may be useful.
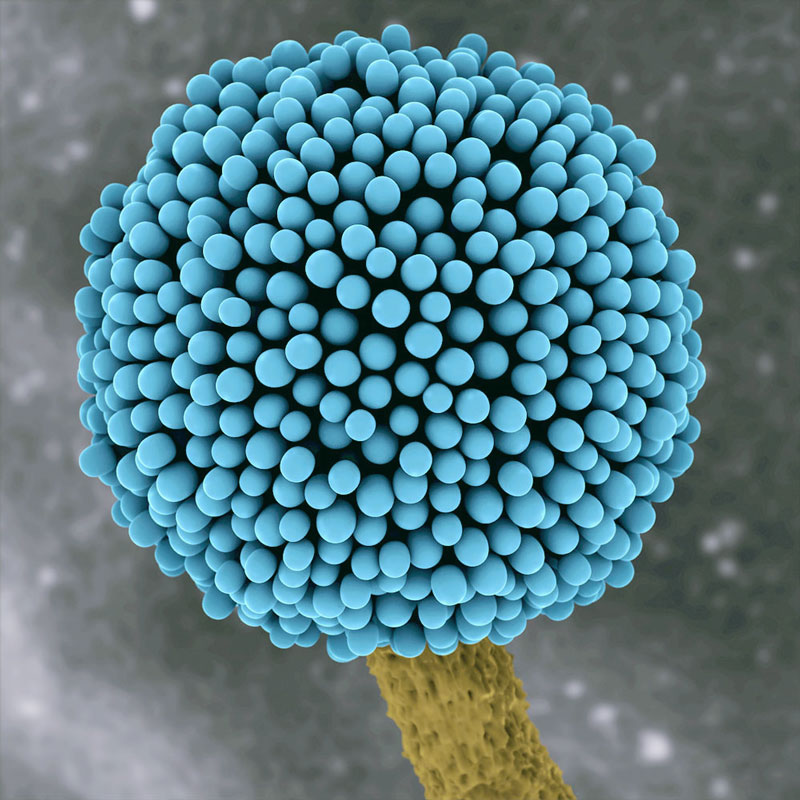
Electron Microscope Image Aspergillus Niger Spore
Organized alphabetically by mold name ( mold genera/species ), these mold spores and their photographs (both on site and under the microscope) have been collected in the U.S., Spain, Mexico, France, as well as in other countries. These are aerobiology laboratory photos of mold under the microscope.
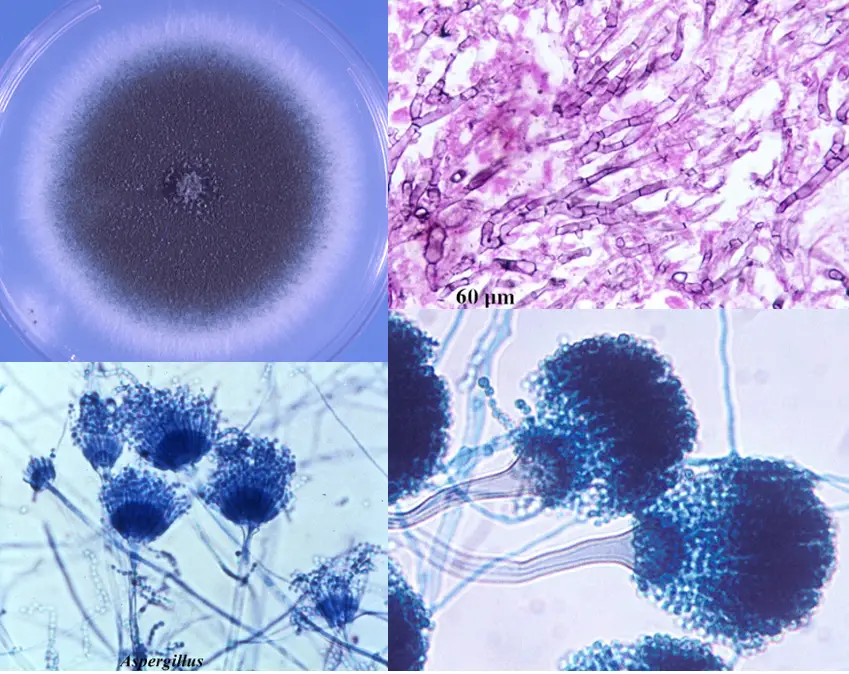
Aspergillus fumigatus Morphology, Pathogenesis, Lab Diagnosis
The biofilm stages included the following: 1) adhesion to the plate surface (4 h), cell co-aggregation and exopolymeric substance (EPS) production; 2) conidial germination into hyphae (8-12 h), development, hyphal elongation, and expansion with channel formation (16-20 h); and 3) biofilm maturation as follows: mycelia development, hyphal layerin.

Aspergillus niger LM 1000x Microscopio t Hongos Plant diseases
Under microscope, A. oryzae is famous by its globose vesicle with elongated conidial chains, which look like fluffy-white strands on the substrate inhibited by A. oryzae (Moubasher 1993). A. oryzae conidiophores are long, arising from substrate, rough-walled, conidial head large, radiate (Fig. 1) with globose to subglobose conidia.

Aspergillus niger a photo on Flickriver
Aspergillus is a fungus that is found in abundance throughout the environment in soil, decomposing plant matter, ornamental plants, water,. The fungus may be visible under a microscope in biopsies of affected tissue. Special stains for fungus may be needed, but other fungi may appear nearly identical..
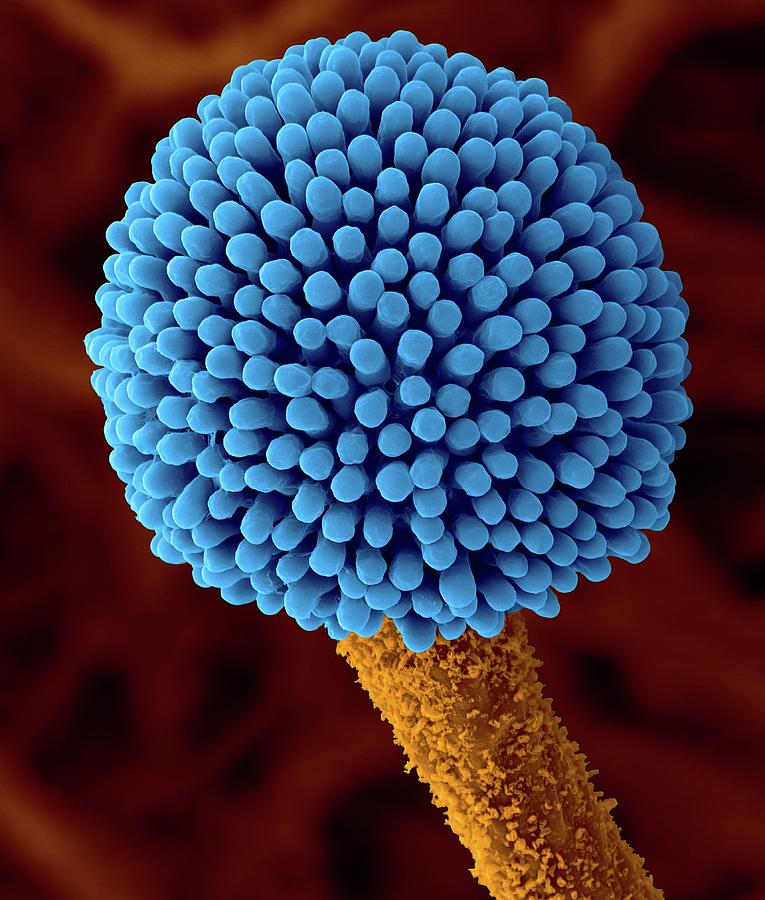
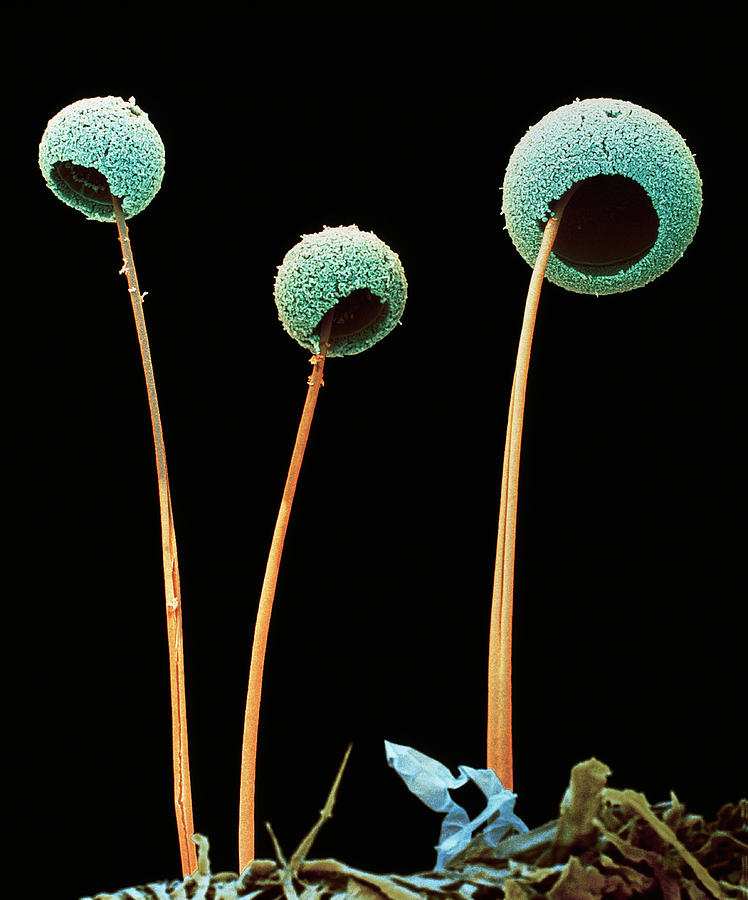
Aspergillus Sp. Fruiting Structure Photograph by Dennis Kunkel
Aspergillus ( / ˌæspərˈdʒɪləs /) is a genus consisting of several hundred mould species found in various climates worldwide. Aspergillus was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli.

Light microscopy of Aspergillus spp with lactophenol cotton blue stain
Healthcare providers may also perform a tissue biopsy, in which a small sample of affected tissue is analyzed in a laboratory for evidence of Aspergillus under a microscope or in a fungal culture. A blood test can help diagnose invasive aspergillosis early in people who have severely weakened immune systems.

Aspergillus Fungus Photograph by Juergen Berger/science Photo Library
H Histopathology of aspergillosis (4 C, 15 F) N Microscopic images of Aspergillus niger (20 F) Media in category "Microscopic images of Aspergillus" The following 47 files are in this category, out of 47 total. 10523 Aspergillus fumigatus.jpg 1,814 × 1,202; 903 KB Antonio e Biagio e Cesare Arrigo Aspergillus fumigatus 01.jpg 640 × 480; 284 KB
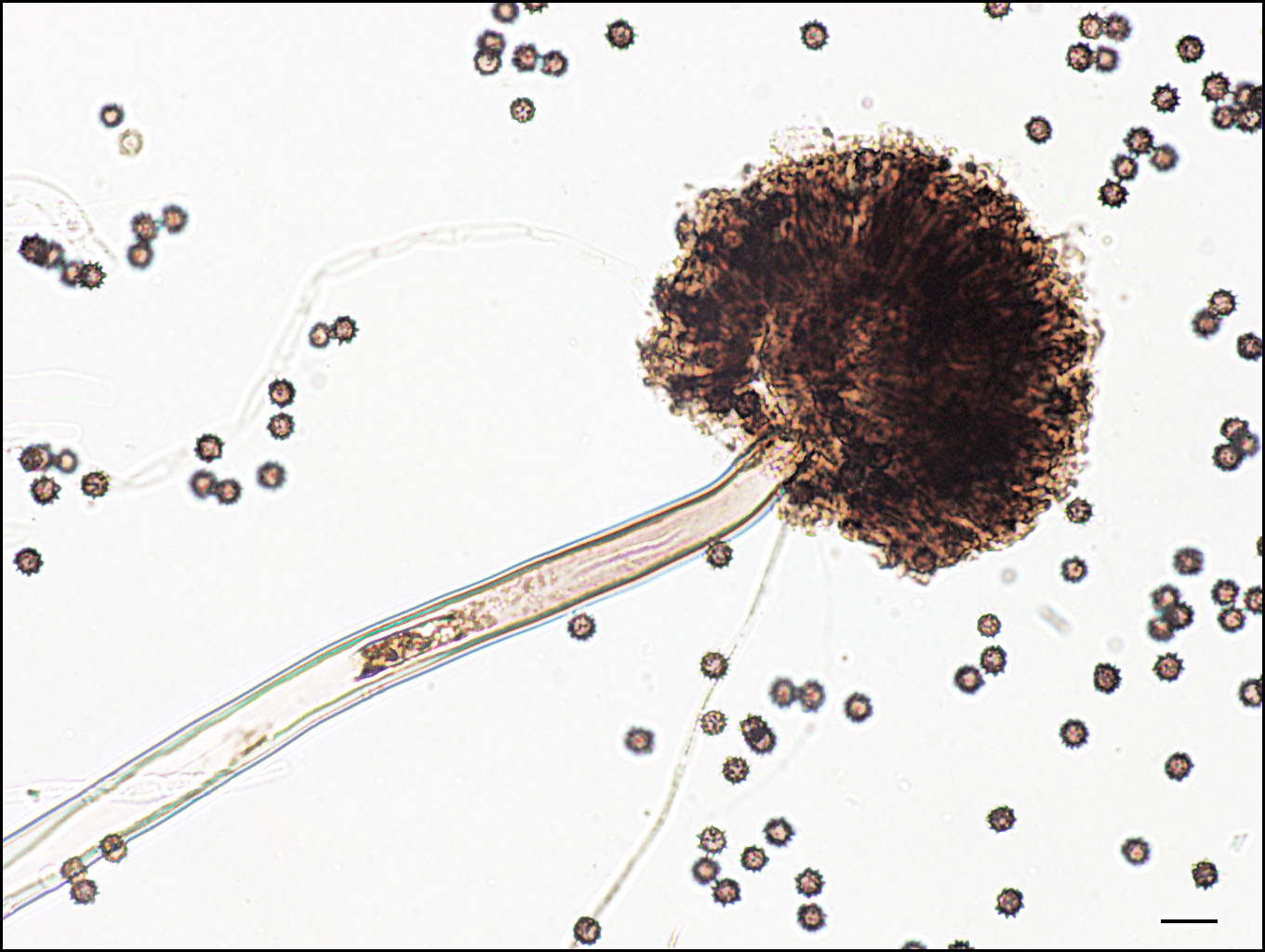
Aspergillus niger Institut national de santé publique du Québec
Abstract Molecular and immunologic tests promise better, faster laboratory diagnosis of aspergillosis, but microscopy and culture remain commonly used and essential tools. Procedural changes, as well as adequate training of laboratory professionals, can enhance the value of these traditional tools.
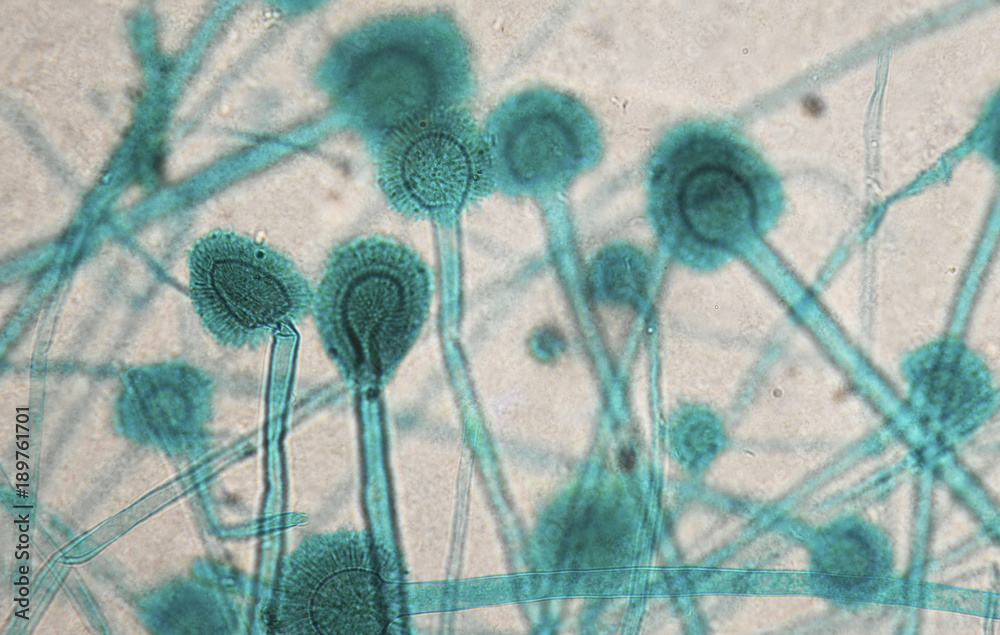
Aspergillus under microscope Stock Photo Adobe Stock
IMAGES OBSERVED UNDER THE MICROSCOPE. Candida albicans Saccharomyces cerevisiae, showing budding cells. Penicillium Aspergillus. Aspergillus. Asexual spores of Rhizopus, along with sexual spores. Rhizopus sporangia with asexual sporangiospores within. GREAT RESOURCE. UC Berkeley's Introduction to Fungi.

Aspergillus versicolor Microbiology, Microscopic cells, Museum of
Pathogenic species in Aspergillus section Fumigati and species delimitation based on polyphasic taxonomy. The most common causative agent of aspergillosis is A. fumigatus with rare reports of invasive infections caused by species of Neosartorya. However, clinical isolates of A. fumigatus are not necessarily morphologically uniform, and mistaken identification of these taxa by morphological.

Ben Amirault, Author at Medicinal Genomics
Aspergillus able to produced biologically active chemical compounds such as antibiotics, mycotoxins. Aspergillus flavus is able to produce mycotoxins as cyclopiazonic acid and Aspergillic acid [9]. Aspergillus is using for the biosynthesis of nanoparticles because it has enough amount of enzymes and it cultured on different medium [10].

Aspergillus flavus conidial heads at various stages of development
Regarding Aspergillus sp., the highest counts were obtained in DG18 (18.38%) and it was not observed in azole-supplemented SDA media. SARS-CoV-2 and the targeted Asper-gillus sections were not.

Microscopic characters of Aspergillus isolates (A) A. flavus; (B) A
Aspergillus (Plural Aspergilli) is a genus of fungi that consists of about 300 identified species of mold (mould). Aspergillus can be found in a variety of environments throughout the world given that their growth is largely determined by the availability of water.