
Sack Of Rome 1527 Banque d'image et photos Alamy
In this illustrated account of the sack of Rome as a cultural and artistic phenomenon, André Chastel reveals the historical ambiguities of preceding events and the traumatic contrast between the flourishing world of art under Pope Clement VII and the city after it was looted by the troops of Emperor Charles V in 1527. Chastel illuminates the cultural repercussions of the humiliation of Rome.

Landsknechts I Sacco di Roma / The Sack of Rome / Złupienie Rzymu (1527)
The Sack destroyed much of Rome, and it is widely seen as ushering in a new era in Italy's history. This article will discuss the impact that the Sack had on Italy and its development. The commonly held belief is that the Sack of Rome ended the Renaissance in Italy. The Sack of Rome in 1527 was of critical importance in the history of Italy.

Roma a ferro e a fuoco. I luoghi del Sacco del 1527 Roma Felix
The Sack of Rome 1527 Home Book Authors: Judith Hook 2345 Accesses 4 Altmetric Sections Table of contents About this book Keywords About the author Bibliographic Information Publish with us Table of contents (20 chapters) Search within book Previous Page of 2 Front Matter Pages N1-xvii PDF Introductions Judith Hook Pages 13-17 Clement VII and Rome

May 6th, 1527 the Sack of Rome Italy's Wonders
Sack of Rome (1527) Coordinates: 41°50′N 12°30′E This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2021) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message)

Sack of Rome (1527) the Triumph of Mannerism in Europe EHNE
In the early morning of May 6, 1527, Charles III, Duke of Bourbon and his forces began their assault on Rome.

12. The 1527 Sack of Rome Lisa Kaborycha
"Hell itself was a more beautiful sight to behold": The Sack of Rome in 1527 - Medievalists.net Advertisement Features "Hell itself was a more beautiful sight to behold": The Sack of Rome in 1527 By Peter Konieczny

Peinture Française du 19ème Siècle The Sack of Rome in 1527 (1835)
The Sack of Rome in May 1527 by the troops of Emperor Charles V—king of Germany, Spain, Naples, and Sicily, and ruler of the Netherlands—was an event of rare violence that left a deep impression during the sixteenth century. An accident of a war opposing a considerable portion of European princes, it partially served as an outlet for.

The Sack of Rome 1527 The Darkest Hour of the Landsknechts YouTube
. Many have interpreted the event as ending the golden age of the High Renaissance, embodied by the works of Raphael and Michelangelo, and hastening the onset of the Counter Reformation and its emphasis on piety and morality. Regardless, the Sack of 1527 was a traumatic event that displaced artisans, artists, and humanists of the papal

IL NUOVO PAPA Il sacco di Roma
On 6 May 1527 the Spanish, German, and Italian troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor and King of Spain, sacked Renaissance Rome. The Sack was a climactic event in the War of the League of Cognac, begun in 1526, and in the broader Italian Wars waged between Spain, France, the Papal States and various Italian city-states between 1494 and 1559.
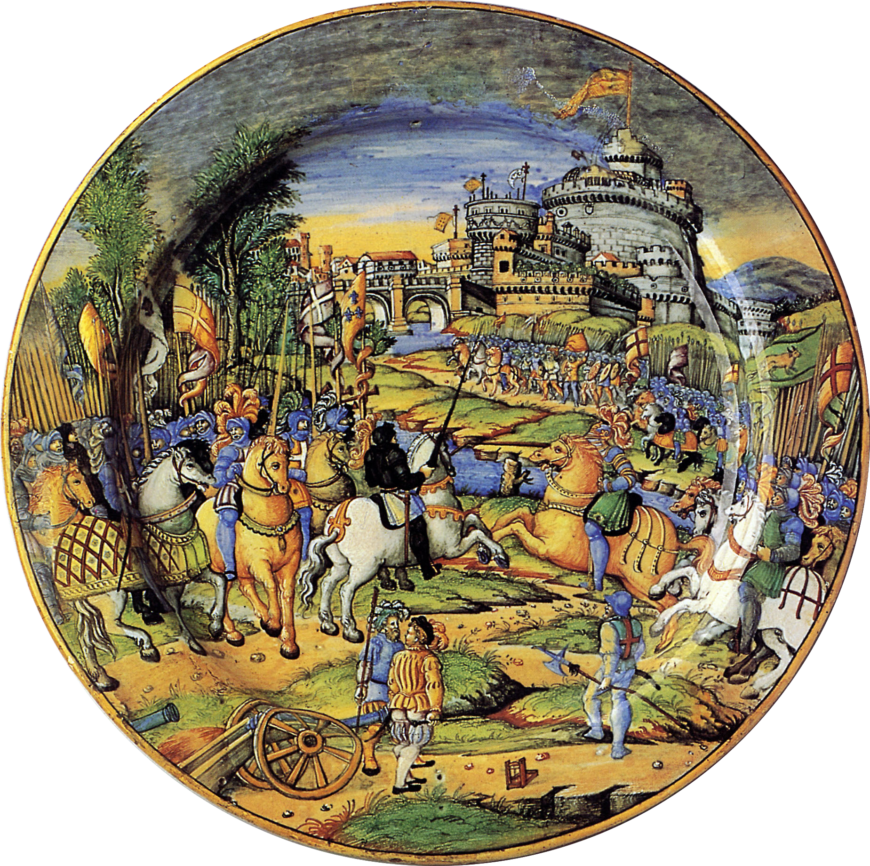

» The Sack of Rome in 1527
Around dawn on 6 May 1527, an imperial army composed primarily of Spanish and German troops besieged the poorly defended city. Their commander, Charles de Bourbon-Montpensier (1490 - 1527), died in the initial assault, but by sunset virtually all of Rome had fallen to his men.

Gothic Sack of Rome Empire Romain, Dark Ages, Ancient History, Les Oeuvres, Gothic, Artist
This video delves into the seismic event of the Sack of Rome in 1527, a pivotal moment that reverberated across Europe. With powerful visuals and historical.

RORATE CÆLI De Mattei The Sack of Rome a merciful chastisement
Sack of Rome, (6 May 1527). Victory over the French at Pavia in 1525 left the forces of the Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V, dominant in Italy. In 1527 these forces stormed the city of Rome and embarked on an orgy of destruction and massacre, terrorizing the population and humiliating Pope Clement VII.

May 6th, 1527 the Sack of Rome Italy's Wonders
The sack of 1527 had an immediate impact due to the rise of recently developed "mass media" (Chastel). Beginning in 1517, the printing press had enabled Luther to spread his ideas. In 1527, Europe followed and either lamented or mocked the trials and tribulations of Rome, the caput mundi ("head of the world") that had suddenly become.

LandsknechtsintheSackofRome15271988byAngusMcBride History, Historical warriors, Warrior
In May 1527, only 17 years after Raphael completed his work, the vast and unruly army of the powerful Emperor Charles V, a motley crew of German, Spaniard and Italian mercenaries, sacked Rome. The assault was brutal and swift: by the time the orgy of bloodletting finally ended, nearly half of the city's population lay dead in the streets.
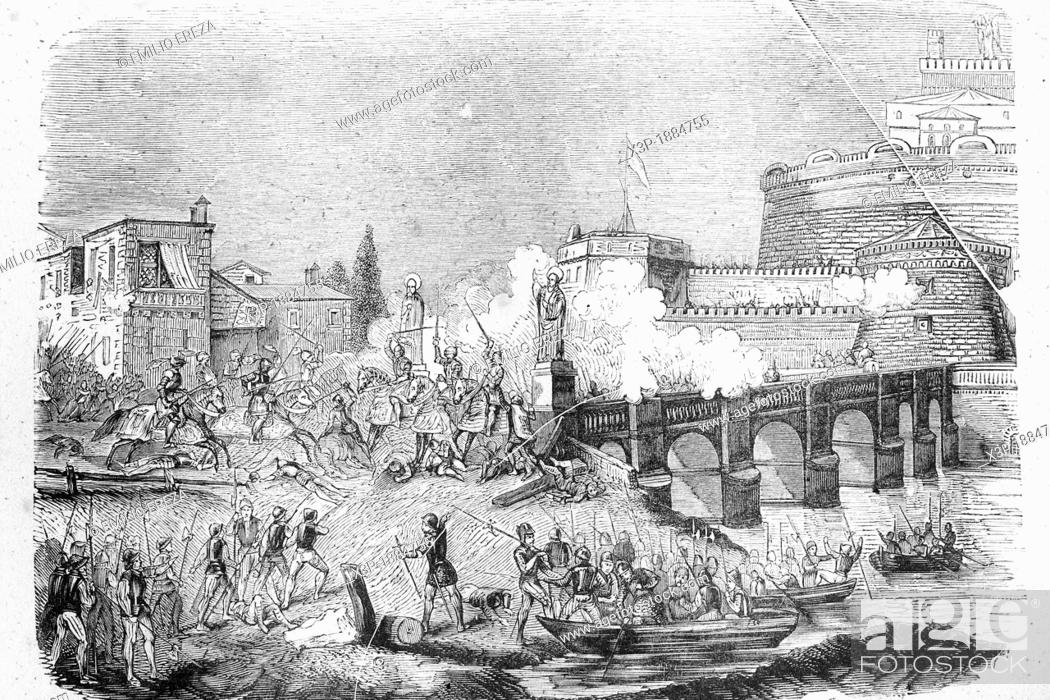
Sack of Rome, 1527 Antique illustration, 1856, Stock Photo, Picture And Rights Managed Image
The Sack of Rome, then part of the Papal States, followed the capture of the city on 6 May 1527 by the mutinous troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor during the War of the League of Cognac. Despite not being ordered to storm the city, with Charles V intending to only use the threat of military action to make Pope Clement VII come to his terms, a largely unpaid Imperial army formed by 14,000.
.jpg)
Flemish School, mid16th Century , The Sack of Rome, 1527 Christie's
About this book. In this illustrated account of the sack of Rome as a cultural and artistic phenomenon, André Chastel reveals the historical ambiguities of preceding events and the traumatic contrast between the flourishing world of art under Pope Clement VII and the city after it was looted by the troops of Emperor Charles V in 1527.