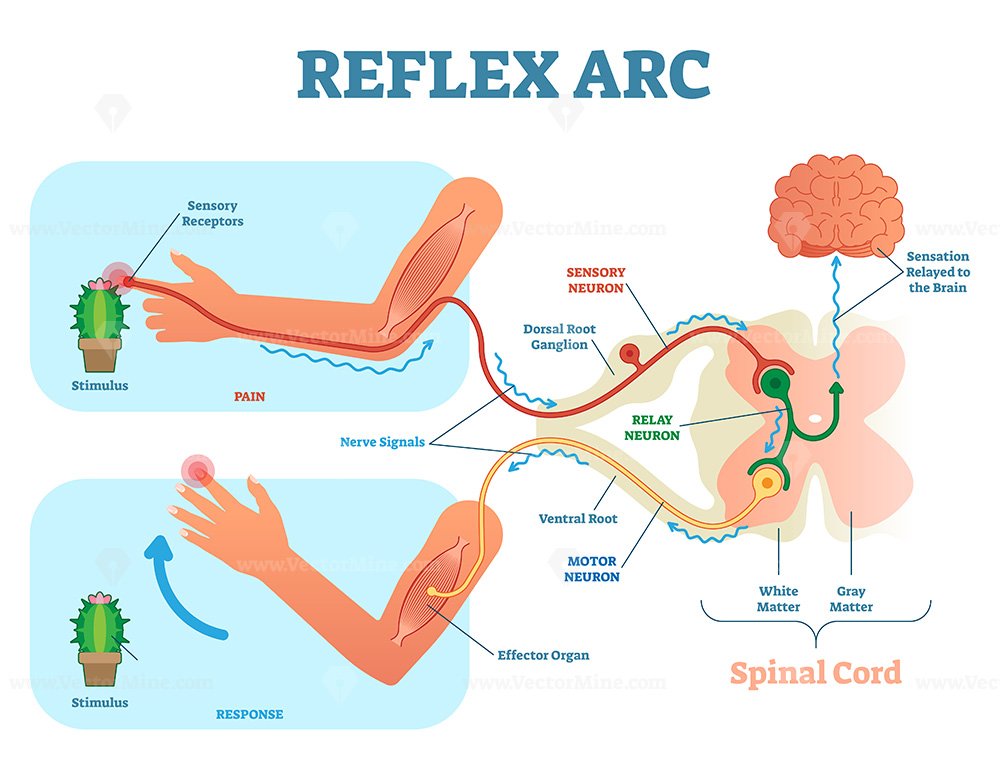
Spinal Reflex Arc anatomical scheme, vector illustration VectorMine
Reflex Arc Components. A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex. Most sensory neurones have a synapse within the spinal cord. This allows for reflexes to take place without the involvement of the central nervous system - speeding up the process. The pathway can be described as a 'reflex arc' which is made up of 5 components:

The top panel in this figure shows a long reflex, where the spinal cord
A reflex arc refers to the neural pathway that a nerve impulse follows. The reflex arc typically consists of five components: A receptor, and independent sensory cell, or an ending of a sensory neuron, reacts to a stimulus (e.g., a stretch receptor).. Circuit diagram for recording electromyograms from the calf muscles. Make sure the ankle.

three neuron ipsilateral reflex arc 2 Diagram Quizlet
A reflex arc occurs when the body responds automatically to an outside stimulation. When someone touches a hot surface, the body responds utilizing a reflex arc to remove the body from the high.

Schematic drawing of the pupillary light reflex pathway. By way of the
Reflex arcs The nerve pathway followed by a reflex action is called a reflex arc . For example, a simple reflex arc happens if we accidentally touch something hot. Receptor in the skin.

Polysynaptic Reflex Arc Diagram Figure 29.1 Diagram Quizlet
The Reflex Arc Quick Navigation [ hide] Introduction Components Receptor Sensory Neuron Interneuron Motor Neuron Effector Organ Types of Reflexes Withdrawal Reflex Receptor Neurons Effector Organ Example Importance Stretch Reflex Muscle Spindle Neurons Neural Circuit Importance Golgi Tendon Reflex Golgi Tendon Organ Neurons Neural Circuit

Reflex Arc Labeling Diagram Quizlet
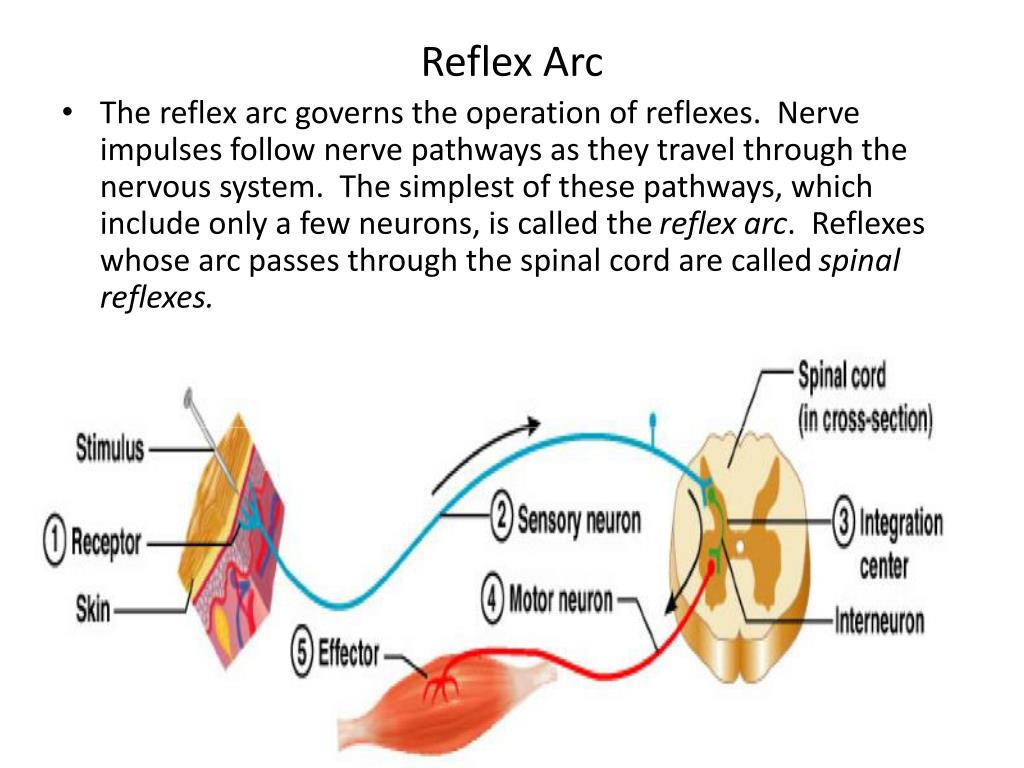
The reflex arc is the pathway that a signal follows from stimulus to response during a reflex action. The typical reflex arc of a simple reflex has seven components, which are shown in Figure 2. Figure 2: A flow chart showing the 7 components of a reflex arc, from the stimulus to the response.

Reflex arc Medical school inspiration, Medical student study, Medical
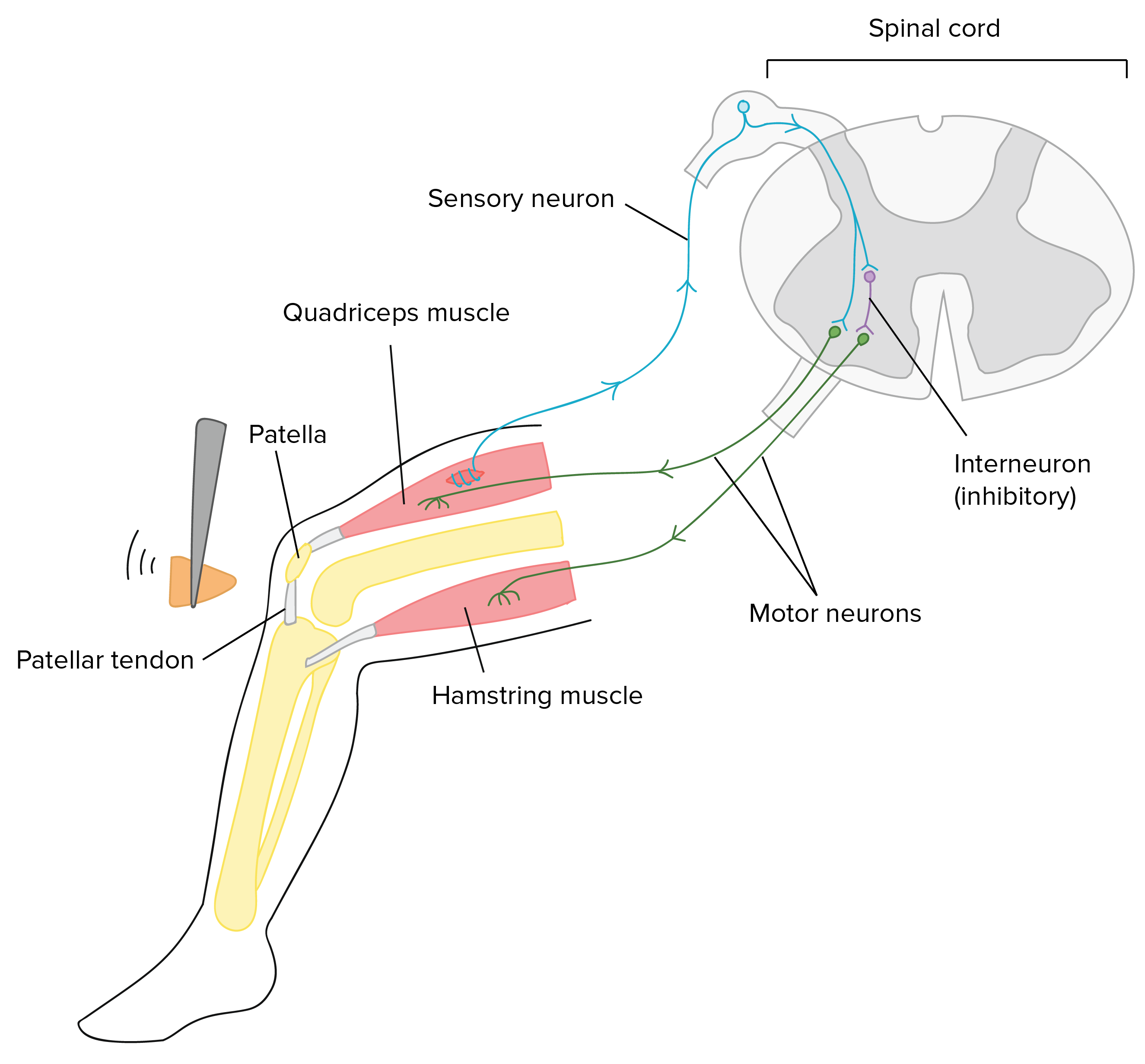
Key Points. Reflexes, or reflex actions, are involuntary, almost instantaneous movements in response to a specific stimulus. Reflex arcs that contain only two neurons, a sensory and a motor neuron, are considered monosynaptic. Examples of monosynaptic reflex arcs in humans include the patellar reflex and the Achilles reflex.
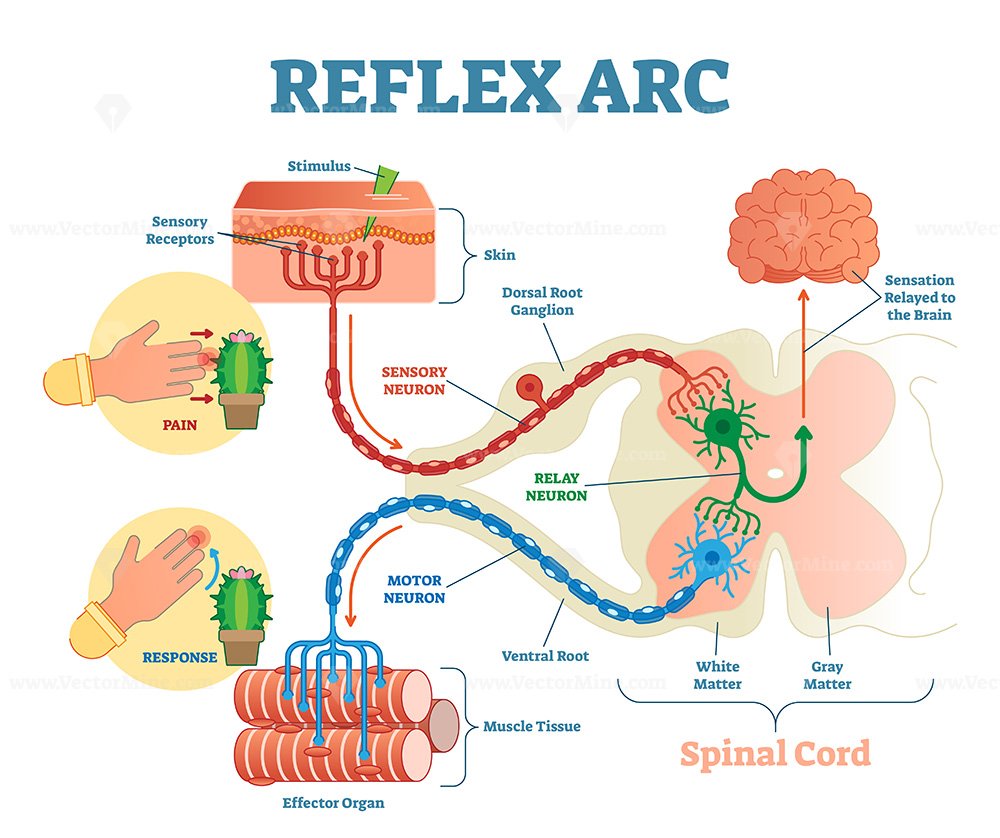
Spinal Reflex Arc anatomical scheme, vector illustration VectorMine
Swallowing, sneezing, and the constriction of the pupil of the eye in bright light are also all reflex actions. The path taken by the nerve impulses in a reflex is called a reflex arc. Most reflex arcs involve only three neurons (see diagram 14.4). The stimulus (a pin in the paw) stimulates the pain receptors of the skin, which initiate an.
😍 Explain a reflex arc. How Does Reflex Arc Work?. 20190129
By definition, a reflex is an involuntary, stereotypical response of the effector tissue from the stimulation of receptors. These reflexes are executed by the successive activation of a certain number of neurons that are mutually connected.

Medical knowledge, Teaching biology, Medical anatomy
The reflex is an automatic response to a stimulus that does not receive or need conscious thought as it occurs through a reflex arc. Reflex arcs act on an impulse before that impulse reaches the brain. [1] Reflex arcs can be Monosynaptic i.e., contain only two neurons, a sensory and a motor neuron.
PPT Reflex Physiology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID313693
The Reflex Arc works through a series of steps that involve a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron. When a stimulus is detected by the sensory neuron, an impulse is sent to the spinal cord, where it is processed by the interneuron. The interneuron then sends an impulse to the motor neuron, which in turn causes a muscle contraction.
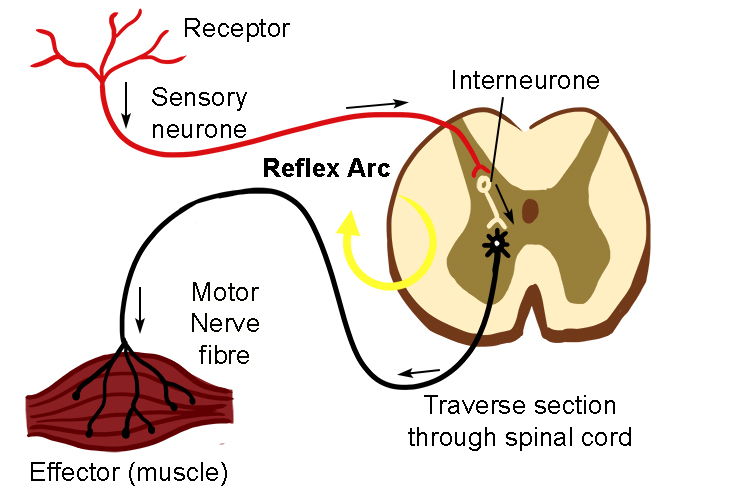
The reflex arc is the short cut of signals through the spine
The simplest reflex arc is the monosynaptic (stretch) reflex. The afferent fibres from the muscle spindles in a muscle enter the dorsal root and proceed to the ventral horn of the spinal cord. There they synapse on motoneurones that project back to the same muscle, or muscles in the same functional group.. Diagram of the paths of afferent.
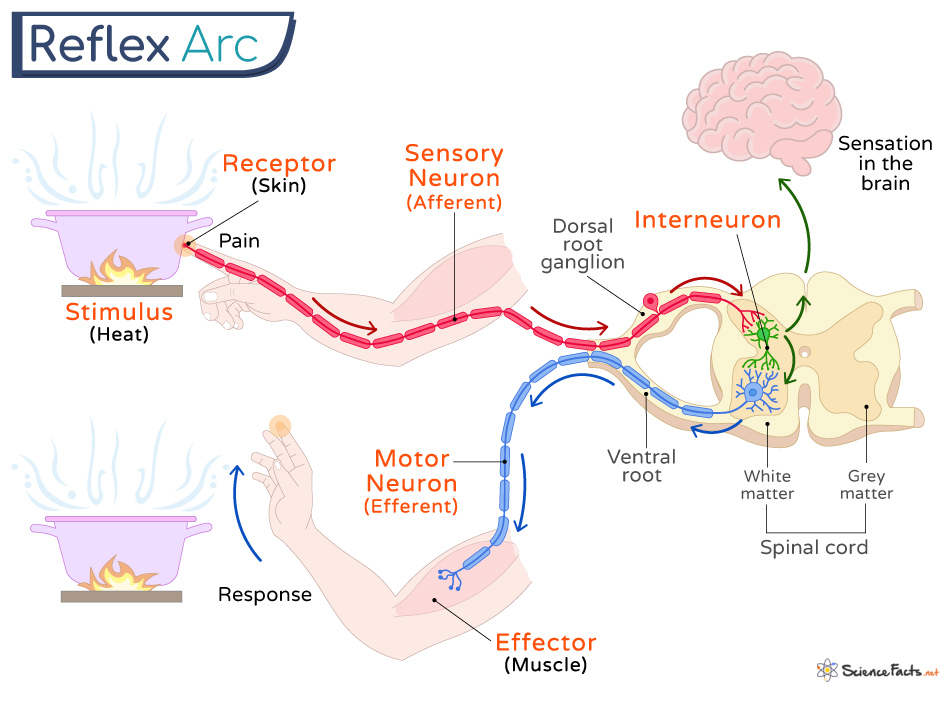
Reflex Arc Definition, Steps, Components, and Diagram
A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex. In vertebrates, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This allows for faster reflex actions to occur by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of routing signals through the brain.

Reflex ARC sensory neuron pathway from stimulus to response outline
The best known of the reflexes is the patellar, or knee-jerk, reflex. The DTR exam involves a healthcare provider tapping your knee with a rubber hammer (it shouldn't hurt). This tap stretches your patellar tendon and the muscle in your thigh that connects to it. That's how the leg moved on its own. Comment.
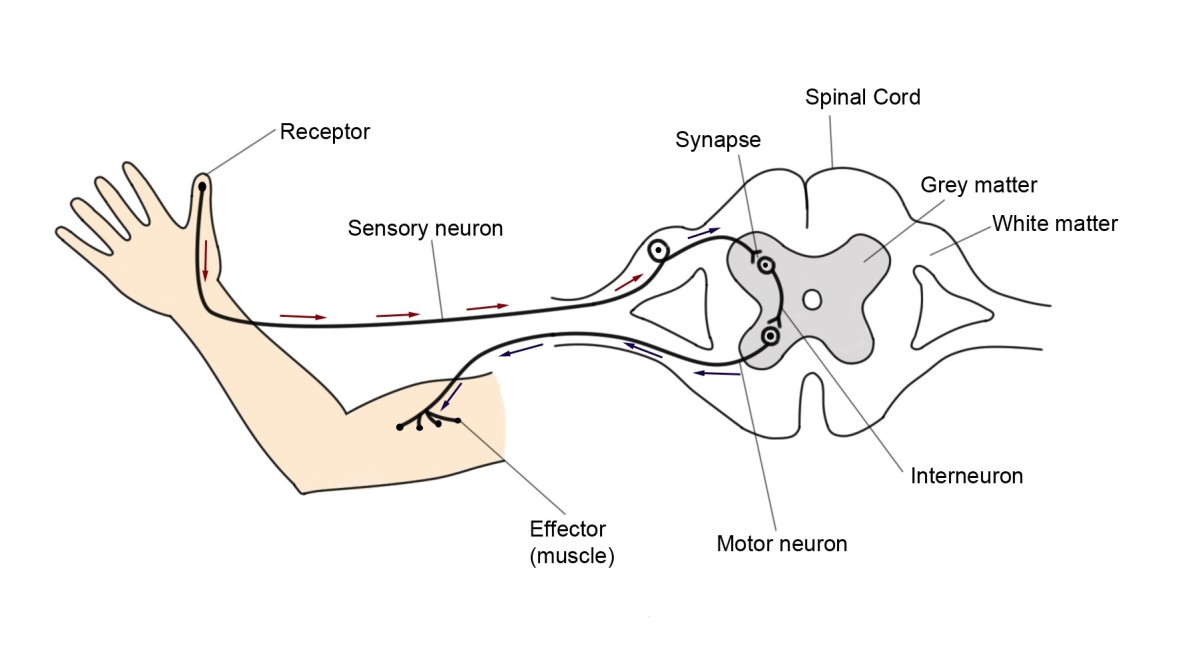
Reflex Action and Reflex Arc What Happens When You Accidentally Touch
Reflex Arc Diagram This labelled diagram of a reflex arc indicates the neural pathway controlling a reflex. It clearly indicates the route adapted when a stimulus occurs and how the reaction takes place.
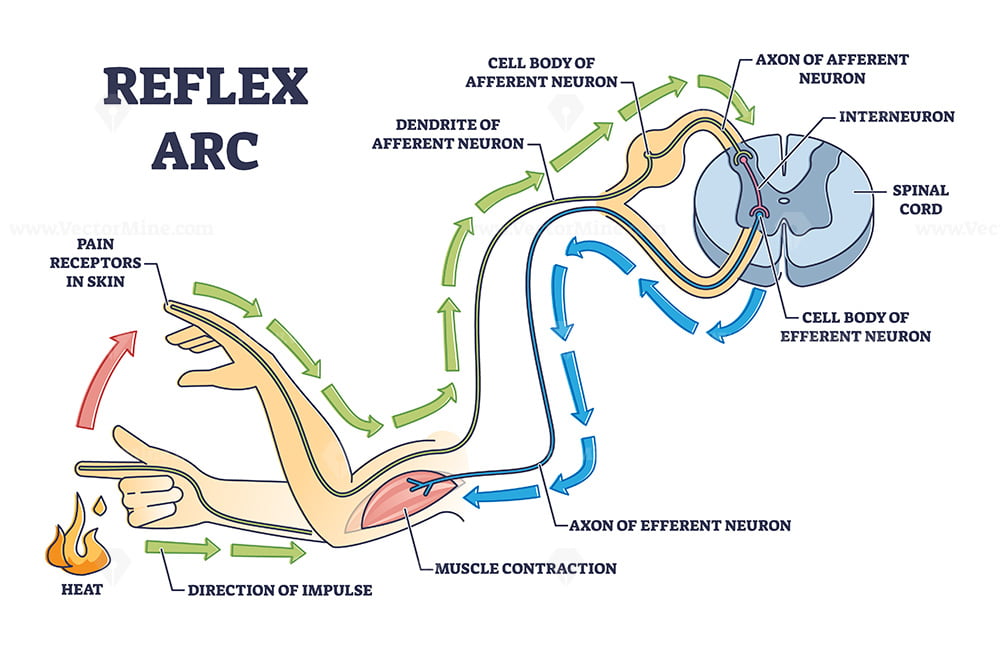
Reflex arc explanation with pain signals and receptor impulse outline
reflex arc, neurological and sensory mechanism that controls a reflex, an immediate response to a particular stimulus. The primary components of the reflex arc are the sensory neurons (or receptors) that receive stimulation and in turn connect to other nerve cells that activate muscle cells (or effectors), which perform the reflex action.